Effects of Phyllostachys edulis Invasion on Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Cunninghamia lanceolata Forest
-
摘要:目的
分析毛竹Phyllostachys edulis入侵杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata林后的细菌群落结构特征,揭示毛竹入侵杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构与林分及土壤环境因子之间的关系。
方法采用高通量测序技术分析毛竹入侵杉木林后土壤细菌群落结构及其与土壤理化因子的相关关系。
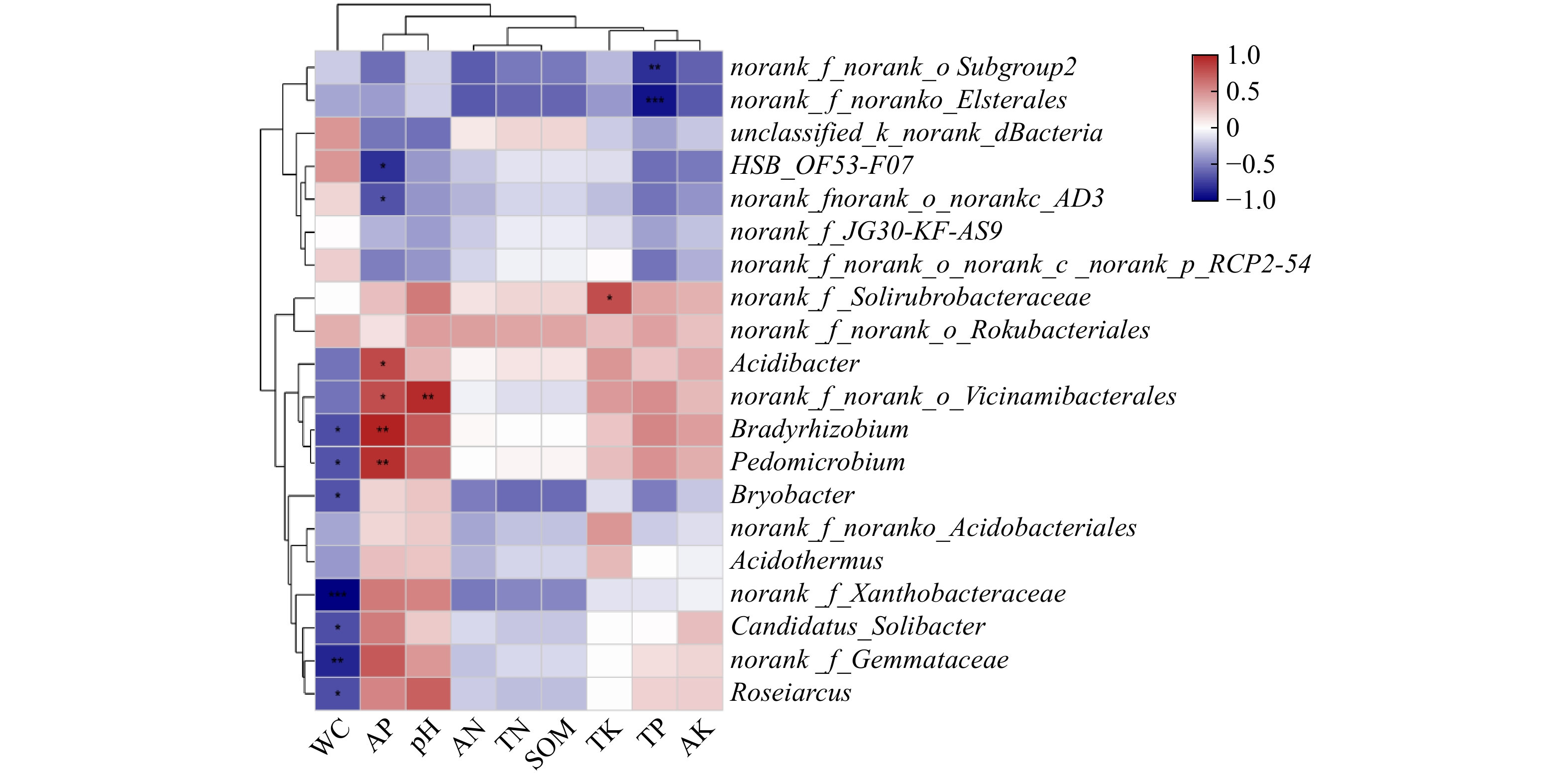
结果3种林型土壤共获得36门108纲241目354科552属2 939个OTU土壤细菌。3种林型土壤中的优势菌门为酸杆菌门Acidobacteria、变形菌门Proteobacteria和绿弯菌门Chloroflexi,3个菌门的相对丰度占总量的71.15%~76.07%。杉木纯林和杉木毛竹混交林土壤酸杆菌门的相对丰度显著高于毛竹纯林土壤酸杆菌门的相对丰度(P<0.05),毛竹纯林和杉木毛竹混交林土壤中变形菌门的相对丰度显著高于杉木纯林土壤中变形菌门的相对丰度(P<0.05),杉木纯林土壤中绿弯菌门的相对丰度显著高于毛竹纯林土壤中绿弯菌门的相对丰度(P<0.05)。从3种林型中鉴别出的相对丰度均大于1%的细菌纲为酸杆菌纲Acidobacteriae、α-变形菌纲Alphaproteobacteria、纤线杆菌纲Ktedonobacteria、浮霉菌纲Planctomycetes、γ-变形菌纲Gammaproteobacteria、放线菌纲Actinobacteria、嗜热油菌纲Thermoleophilia、Vicinamibacteria和酸微菌纲Acidimicrobiia。优势菌纲为酸杆菌纲和α-变形菌纲。3种林型中鉴别出的相对丰度在1%以上的细菌属为HSB_OF53-F07、热酸菌属Acidothermus、念珠菌固体杆菌属Candidatus_Solibacter、酸杆菌属Acidibacter、Bryobacter和慢生根瘤菌属Bradyrhizobium。优势菌属和土壤环境因子的Spearman相关性分析表明,土壤含水率和有效磷含量是影响土壤细菌群落的主要因子。
结论毛竹入侵杉木林后对土壤细菌群落有显著影响,杉木毛竹混交林和毛竹纯林土壤中单独出现的非优势菌属可为研究毛竹入侵杉木林过程中土壤细菌群落的变化提供重要参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis paper aims to elucidate the impacts of soil bacterial community structure after Phyllostachys edulis invaded Cunninghamia lanceolata forest, and reveals the relationship between bacterial community diversity and structure and forest types as well as soil environment factors.
MethodIllumina MiSeq high throughput sequencing and OTU analysis were used to assess the soil bacterial community structure and its correlation with soil physical and chemical factors in Cunninghamia lanceolata forest invaded by Phyllostachys edulis (CP) to compare with that in Phyllostachys edulis forest (PF) and Cunninghamia lanceolata forest (CF).
ResultA total of
2939 OTU soil bacteria of 36 phyla, 108 classes, 241 orders, 354 families, 552 genera were obtained from this 3 forest stand samples, among them Acidobacteria, Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi were the predominant bacterial phyla, accounting for 71.15%-76.07%. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria in CF and CP was significantly higher than that in PF(P<0.05), the relative abundance of Proteobacteria in CF was significantly lower than that in other two forests, the relative abundance of Chloroflexi in CF was significantly higher than that in PF. The bacteria with relative abundance of more than 1% identified in the 3 forest sample plots are: Acidobacteriia, Alphaproteobacteria, Ktedonobacteria, Planctomycetes, Gammaproteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Thermoleophilia, Vicinamibacteria and Acidimicrobiia, Acidobacteriia and Alphaproteobacteria are two dominant classes. The bacterial genera with relative abundance of more than 1% identified in the 3 forests are: HSB_OF53-F07, Acidothermus, Candidatus Solibacter, Acidobacterium, Bryobacter and Bradyrhizobium. Spearman correlation analysis between dominant bacterial genera and soil environmental factors showed that, soil water content and available phosphorus are the main factors affecting soil bacterial community.ConclusionThe invasion of Phyllostachys edulis into the Cunninghamia lanceolata forest has a significant impact on the soil bacterial community. The non-dominant bacteria isolated from the CP and the PF can provide an important reference for studying the changes of bacterial community during this intrusion process.
-
铁线莲属Clematis植物是一种集观赏和药用于一身的特色植物,也是近年来最为流行的花园植物之一。铁线莲花色丰富、花型各异、种类繁多、花期长,具有良好的攀援依附特性,既可作为风格别致的盆栽花卉,也可用于墙体、拱门、花柱等立体垂直绿化,还可作切花、地被等应用,有“藤本皇后”之美称[1-2]。
涝渍胁迫是传统的农业气象灾害之一,在中国南方地区尤其是长江中下游地区,由于降水量过多、地下水位过高、土壤排水不良等原因,常发生涝渍灾害,对植物外部形态和生理生化等方面产生严重影响[3-4]。目前,国内市场铁线莲品种多为欧洲选育的园艺品种,随着铁线莲栽培应用的增加,源自温带冷凉气候区的铁线莲品种适应性问题开始显现。在江浙地区栽培后表现出明显的不适应性,尤其是不耐水湿,绝大多数品种无法抵御长期雨水天气,易滋生病虫害,呈现叶片萎蔫脱落、茎秆枯萎等现象。长期的涝渍胁迫可导致铁线莲整株死亡,极大地限制了铁线莲的推广应用。
本研究中,采用盆栽模拟涝渍处理调查了43个铁线莲品种在涝渍胁迫下的表现,通过对叶片、茎秆等形态指标的观察,对叶绿素含量、相对电导率等生理指标的测定,开展耐涝性鉴定,筛选耐涝种质资源,建立一个简单可行的耐涝性评价方法,为铁线莲耐涝评价及抗性育种提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验材料为保存于浙江省亚热带作物研究所国家铁线莲种质资源库的铁线莲园艺品种43个(表1)。43个品种铁线莲均为长势一致、健康、无病虫害的3年生植株,盆径为11 cm,盆高为18 cm,采用泥炭∶椰糠∶珍珠岩∶轻石比例为55∶15∶15∶15的基质,连栋温室栽培,正常肥水管理。
表 1 供试试验材料Table 1. Plant materials used in this study序号 品种 来源 序号 品种 来源 1 ‘小鸭’‘Piilu’ 爱沙尼亚 23 ‘志愿者’ ‘Volunteer’ 英国 2 ‘红衣主教’ ‘Rouge Cardinal’ 法国 24 ‘别致’ ‘Bieszczady’ 英国 3 ‘琉璃’ ‘Ruriokoshi’ 日本 25 ‘红星’ ‘Red Star’ 日本 4 ‘包查德女伯爵’ ‘Comtesse de Bouchaud’ 法国 26 ‘变心’ ‘Change of Heart’ 波兰 5 ‘倒影’ ‘Reflections’ 英国 27 ‘爱莎’ ‘Asao’ 日本 6 ‘多蓝’‘Multi Blue’ 荷兰 28 ‘瑞贝卡’ ‘Rebecca’ 英国 7 ‘乌托邦’ ‘Utopia’ 日本 29 ‘神秘面纱’ ‘Night Veil’ 日本 8 ‘宝石蓝光’ ‘Blue Light’ 荷兰 30 ‘努比亚’ ‘Nubia’ 英国 9 ‘黎明的天空’ ‘Dawn’ 波兰 31 ‘薇安’ ‘Vyvyan Pennell’ 英国 10 ‘水晶喷泉’ ‘Crystal Fountain’ 日本 32 ‘里昂村庄’ ‘Ville de Lyon’ 法国 11 ‘繁星’ ‘Nelly Moser’ 法国 33 ‘莎拉芬娜’ ‘Serafina’ 波兰 12 ‘天幕坠落’ ‘Skyfall’ 波兰 34 ‘撒玛利亚’ ‘Samaritan Jo’ 英国 13 ‘波罗尼亚’ ‘Viva Polonia’ 波兰 35 ‘丹空’ ‘Yuan’ 日本 14 ‘向阳’ ‘Sunny Side’ 日本 36 ‘钻石球’ ‘Diamond Ball’ 波兰 15 ‘斯丽’‘Thyrislund’ 英国 37 ‘哥白尼’ ‘Kopernik’ 波兰 16 ‘粉香槟’ ‘Pink Champagne’ 日本 38 ‘薇妮沙’ ‘Venosa Violacea’ 法国 17 ‘白王冠’ ‘Hakaookan’ 日本 39 ‘欧啦啦’ ‘Ooh La La’ 英国 18 ‘钻石’ ‘Diamantina’ 英国 40 ‘倪碧欧’ ‘Niobe’ 波兰 19 ‘蜥蜴’ ‘Basilisk’ 日本 41 ‘朱莉安’ ‘Juliane’ 英国 20 ‘金银丝’ ‘Filigree’ 英国 42 ‘玛丽’ ‘Mary Rose’ 英国 21 ‘大河’ ‘Taiga’ 日本 43 ‘中国红’ ‘Westerplatte’ 波兰 22 ‘巴黎风情’ ‘Parisienne’ 英国 1.2 试验方法
试验于2022年5—7月在温室大棚内进行,温度为15℃ ~ 35℃,空气湿度为45% ~ 55%,采用双套盆法进行淹水胁迫。试验设置2个处理,分别为对照与淹水处理:(1)对照组(CK),每天16:00—17:00进行浇水,保持土壤含水量在50%~60%,直至试验结束;(2)淹水处理(T),将盆栽铁线莲放置于塑料周转箱中(长×宽×高为42.0 cm×31.5 cm×22.5 cm),保持水位高于土面4~5 cm,定时补水,每7 d更换一次周转箱内的水,持续淹水14 d,观察并记录植株生长特性。采用完全随机区组设计,试验做3次生物学重复,设置对照组与淹水处理,每品种每处理5盆,每盆定植铁线莲1株。
1.3 数据处理
参考汤肖玮等[5]茶用菊耐涝性综合评价及尹冬梅等[6]建立的菊花耐涝评价体系,依据淹水胁迫后观测记录的铁线莲表型特性,将表型量化进行打分,建立铁线莲的耐涝渍胁迫表型性状量化评分体系。
采用Microsoft Excel 2016软件进行数据分析,采用SPSS 22.0软件进行相关性分析,采用R3.5.3进行聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 淹水处理后铁线莲园艺品种的表型变化
在淹水胁迫处理的前7 d,43个铁线莲园艺品种均未出现受胁迫表型。随着淹水时间的增加,‘小鸭’‘乌托邦’‘大河’‘努比亚’‘志愿者’‘钻石球’等品种的叶片从下部开始出现萎蔫下垂、叶片变黄现象,逐步向中上部叶片蔓延,淹水处的茎秆颜色逐渐发黑。淹水胁迫处理14 d后,绝大部分铁线莲园艺品种均出现叶片萎蔫下垂并黄化现象,‘小鸭’‘乌托邦’‘金银丝’‘大河’‘志愿者’‘努比亚’‘钻石球’‘倪欧碧’8个品种的茎秆水渍化腐烂,而‘别致’‘巴黎风情’‘天幕坠落’‘向阳’和 ‘神秘面纱’的胁迫程度较轻。
2.2 铁线莲耐涝形态指标量化评价体系的建立
参考聂功平等[7]百合(lilium spp.)耐涝表型性状综合评价体系与SU等[8]建立的菊花Chrysanthemum morifolium耐涝性评价体系,结合铁线莲园艺品种盆栽苗在持续淹水胁迫过程中的表型变化,根据叶片形态、叶片颜色、淹水处茎色和茎形态的差异,将铁线莲受涝渍胁迫后的表型分为不同等级,并进行量化评分,评价标准见表2、表3。
表 2 叶片形态指标定级范围及得分标准Table 2. Leaf morphology index rating range and scoring criteria实测值定级范围 形态 颜色 叶片形态 得分/分 叶颜色 得分/分 Ⅰ 叶片自然伸展 7 全株叶片绿色 5 Ⅱ 植株下层叶片萎蔫下垂 6 近水处边缘失绿 4 Ⅲ 植株中下层叶片萎蔫下垂 5 黄色或褐色腐烂叶<1/3 3 Ⅳ 植株上层叶片稍萎蔫,中下层叶片萎蔫下垂 4 黄色或褐色腐烂叶1/3~~1/2 2 Ⅴ 全株叶片萎蔫下垂 3 黄色或褐色腐烂叶>1/2 1 Ⅵ 植株下层叶片腐烂,中上层叶片干枯、褶皱 2 Ⅶ 大部分叶片干枯腐烂 1 表 3 茎形态指标定级范围及得分标准Table 3. Stem morphology index rating range and scoring criteria实测值定级范围 形态 颜色 茎形态 得分/分 茎颜色 得分/分 Ⅰ 正常 4 自然色 4 Ⅱ 表面水渍状膨大 3 浅褐色 3 Ⅲ 水渍状肥肿 2 褐化 2 Ⅳ 水渍状腐烂 1 发黑 1 2.3 铁线莲园艺品种耐涝性分析
2.3.1 综合评分结果
43个铁线莲园艺品种涝害表型量化后综合评分结果如表4所示。由表4可知,43个铁线莲园艺品种中,‘小鸭’‘乌托邦’‘大河’‘志愿者’‘变心’‘努比亚’‘钻石球’‘倪碧欧’的综合评分最低,均为4分,‘别致’的综合评分最高,为20分,其次为‘巴黎风情’,综合评分为17分,‘天幕坠落’‘向阳’‘神秘面纱’居第三位,综合评分均为16分。各个品种综合评分差异较大,表明铁线莲不同品种耐涝性强弱差异较大。
表 4 43个铁线莲园艺品种形态涝害指数得分Table 4. Morphological waterlogging damage index scores of 43 Clematis.序号 品种 各评价指标/分 综合评分/分 评价等级 叶形态 叶色 茎形态 茎色 1 ‘小鸭’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 2 ‘红衣主教’ 4 3 3 4 14 Ⅱ 3 ‘琉璃’ 4 3 3 2 12 Ⅱ 4 ‘包查德女伯爵’ 5 2 4 4 15 Ⅱ 5 ‘倒影’ 2 1 4 3 10 Ⅲ 6 ‘多蓝’ 5 3 4 1 13 Ⅱ 7 ‘乌托邦’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 8 ‘蓝光’ 4 2 3 4 13 Ⅱ 9 ‘黎明的天空’ 5 2 4 4 15 Ⅱ 10 ‘水晶喷泉’ 2 1 2 1 6 Ⅳ 11 ‘繁星’ 3 1 4 1 9 Ⅲ 12 ‘天幕坠落’ 5 3 4 4 16 Ⅱ 13 ‘波罗尼亚’ 3 5 2 3 13 Ⅱ 14 ‘向阳’ 5 3 4 4 16 Ⅱ 15 ‘斯丽’ 1 1 4 2 8 Ⅲ 16 ‘粉香槟’ 2 1 4 1 8 Ⅲ 17 ‘白王冠’ 2 2 2 1 7 Ⅳ 18 ‘钻石’ 2 2 2 1 7 Ⅳ 19 ‘蜥蜴’ 2 1 4 2 9 Ⅲ 20 ‘金银丝’ 2 1 1 1 5 Ⅳ 21 ‘大河’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 22 ‘巴黎风情’ 6 3 4 4 17 Ⅰ 23 ‘志愿者’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 24 ‘别致’ 7 5 4 4 20 Ⅰ 25 ‘红星’ 1 1 3 1 6 Ⅳ 26 ‘变心’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 27 ‘爱莎’ 3 2 2 1 8 Ⅲ 28 ‘瑞贝卡’ 2 1 2 1 6 Ⅳ 29 ‘神秘面纱’ 5 3 4 4 16 Ⅱ 30 ‘努比亚’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 31 ‘薇安’ 1 1 2 1 5 Ⅳ 32 ‘里昂村庄’ 5 3 3 2 13 Ⅱ 33 ‘塞拉菲娜’ 4 2 4 3 13 Ⅱ 34 ‘撒玛利亚’ 3 2 4 3 12 Ⅱ 35 ‘円空’ 2 2 2 1 7 Ⅳ 36 ‘钻石球’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 37 ‘哥白尼’ 3 3 4 3 13 Ⅱ 38 ‘薇尼莎’ 6 3 3 1 13 Ⅱ 39 ‘哦啦啦’ 2 1 2 1 6 Ⅳ 40 ‘倪欧碧’ 1 1 1 1 4 Ⅳ 41 ‘朱莉安’ 3 2 4 3 12 Ⅱ 42 ‘玛丽玫瑰’ 1 1 2 1 5 Ⅳ 43 ‘中国红’ 1 2 2 2 7 Ⅳ 2.3.2 相对含水量、相对电导率与叶绿素含量测定结果
通过对43个铁线莲园艺品种叶片的相对含水量、相对电导率与叶绿素含量进行测定(表5),发现涝渍胁迫后铁线莲叶片相对含水量降低,其中‘乌托邦’‘巴黎风情’‘红星’‘斯丽’‘玛丽’叶片相对含水量降低较多,分别比CK降低了22.72%、19.65%、16.50%、16.40%与14.39%。长期涝渍胁迫会导致铁线莲叶片相对电导率增加,其中‘金银丝’‘斯丽’‘白王冠’‘红星’‘瑞贝卡’在涝渍胁迫14 d后叶片相对电导率分别比CK增加了294.61%、292.48%、242.42%、218.63%和213.98%。涝渍胁迫导致铁线莲叶片中叶绿素含量降低,其中‘努比亚’‘志愿者’‘撒玛利亚’‘波罗尼亚’和‘白王冠’叶片中叶绿素含量分别比CK降低了98.82%、95.46%、61.56%、57.94%和48.67%(表5)。
表 5 43个铁线莲园艺品种主要生理指标Table 5. Main physiological indexes of 43 Clematis.序号 品种 相对含水量/% 相对电导率/(mS·cm−1) 叶绿素a/(mg·g−1) 叶绿素b/(mg·g−1) 总叶绿素/(mg·g−1) 类胡萝卜素/(mg·g−1) CK T CK T CK T CK T CK T CK T 1 ‘小鸭’ 87.29±0.45 76.68±0.48 34.29±1.60 72.31±2.60 2.80±0.05 1.83±0.02 1.64±0.04 1.02±0.01 4.47±0.09 2.87±0.03 10.86±0.21 7.22±0.07 2 ‘红衣主教’ 78.69±0.20 73.95±0.56 50.64±1.77 52.72±0.43 2.59±0.04 2.36±0.02 1.39±0.03 1.29±0.01 4.01±0.07 3.67±0.04 10.10±0.18 9.11±0.09 3 ‘琉璃’ 83.14±0.41 78.41±0.09 26.32±0.45 38.96±0.51 2.45±0.04 1.75±0.08 1.27±0.02 0.93±0.05 3.75±0.06 2.70±0.13 9.50±0.17 7.06±0.33 4 ‘包查德女伯爵’ 83.33±0.19 81.19±0.29 34.45±0.21 50.33±2.79 2.48±0.03 1.40±0.05 1.37±0.02 0.78±0.03 3.88±0.05 2.19±0.08 9.59±0.12 5.41±0.18 5 ‘倒影’ 76.52±0.76 74.91±0.37 41.67±1.29 53.87±1.81 2.87±0.04 1.92±0.05 1.75±0.04 1.02±0.03 4.65±0.08 2.95±0.08 11.35±0.19 7.39±0.24 6 ‘多蓝’ 82.52±0.29 79.51±0.67 26.34±0.34 35.38±0.79 1.91±0.05 1.17±0.03 1.08±0.03 0.59±0.02 3.01±0.08 1.78±0.05 7.75±0.22 4.44±0.12 7 ‘乌托邦’ 77.24±0.73 54.52±0.55 32.50±0.41 93.20±0.44 2.27±0.06 1.97±0.07 1.24±0.04 1.12±0.04 3.53±0.10 3.11±0.11 8.99±0.27 8.87±0.31 8 ‘蓝光’ 79.88±0.38 79.62±0.34 35.45±0.38 38.62±0.57 1.82±0.07 1.14±0.04 0.96±0.03 0.62±0.02 2.80±0.10 1.77±0.06 7.00±0.23 4.61±0.16 9 ‘黎明的天空’ 85.22±0.25 80.58±0.16 35.92±0.93 55.09±2.38 2.54±0.03 1.63±0.11 1.35±0.02 0.91±0.06 3.92±0.05 2.56±0.17 9.69±0.11 7.02±0.48 10 ‘水晶喷泉’ 80.80±0.17 77.88±0.14 44.91±0.59 67.54±0.91 2.43±0.02 1.48±0.04 1.30±0.01 0.83±0.02 3.76±0.03 2.33±0.06 9.40±0.09 5.95±0.18 11 ‘繁星’ 79.49±0.42 74.85±0.26 32.72±0.27 85.13±0.76 2.04±0.05 1.37±0.02 1.10±0.03 0.74±0.01 3.16±0.08 2.12±0.03 8.06±0.20 5.90±0.08 12 ‘天幕坠落’ 82.79±0.06 76.84±0.23 49.66±0.81 51.12±0.51 2.24±0.03 1.51±0.03 1.19±0.02 0.83±0.02 3.45±0.04 2.35±0.05 8.57±0.11 5.87±0.13 13 ‘波罗尼亚’ 81.69±0.08 77.14±0.51 28.86±0.41 48.76±0.89 2.33±0.06 0.97±0.02 1.23±0.04 0.52±0.01 3.59±0.10 1.51±0.03 8.85±0.26 4.08±0.07 14 ‘向阳’ 83.19±0.25 78.45±0.28 27.26±0.60 40.53±1.35 2.11±0.06 1.50±0.02 1.11±0.03 0.82±0.01 3.25±0.09 2.34±0.04 8.16±0.23 6.04±0.10 15 ‘斯丽’ 83.70±0.18 67.30±2.13 23.36±0.35 91.67±0.73 1.85±0.08 1.07±0.01 1.01±0.05 0.57±0.01 2.88±0.13 1.64±0.02 7.27±0.31 4.42±0.05 16 ‘粉香槟’ 80.75±0.07 75.13±0.43 30.83±0.27 41.70±1.28 2.23±0.06 1.72±0.03 1.22±0.03 0.98±0.02 3.47±0.09 2.72±0.04 8.54±0.22 6.76±0.11 17 ‘白王冠’ 80.78±0.53 70.21±0.18 26.71±0.44 91.47±1.43 1.92±0.05 0.98±0.05 1.05±0.03 0.55±0.03 3.00±0.08 1.54±0.08 7.35±0.19 4.24±0.20 18 ‘钻石’ 79.80±0.19 79.30±0.37 33.68±0.64 79.28±1.58 1.88±0.08 0.72±0.01 1.04±0.04 0.40±0.01 2.94±0.12 1.13±0.02 7.39±0.30 3.34±0.06 19 ‘蜥蜴’ 79.35±0.36 71.37±0.47 34.26±1.02 69.02±0.82 2.65±0.07 2.54±0.02 1.50±0.04 1.43±0.02 4.18±0.11 4.00±0.04 10.41±0.28 10.18±0.11 20 ‘金银丝’ 78.14±1.93 68.27±1.48 25.20±0.08 99.43±0.36 1.91±0.03 1.72±0.05 1.06±0.02 0.94±0.03 2.99±0.05 2.68±0.07 7.22±0.13 6.64±0.17 21 ‘大河’ 78.25±0.16 76.57±0.89 27.99±0.46 52.48±1.25 2.28±0.05 2.12±0.05 1.29±0.03 1.16±0.03 3.59±0.09 3.30±0.08 9.63±0.22 8.87±0.22 22 ‘巴黎风情’ 56.80±3.94 37.15±7.63 91.42±0.84 98.69±0.20 2.24±0.03 1.99±0.02 1.28±0.01 1.19±0.01 3.54±0.04 3.20±0.03 8.62±0.07 7.73±0.04 23 ‘志愿者’ 81.08±2.00 80.49±2.02 45.25±0.29 70.25±0.46 2.77±1.16 0.04±0.01 1.45±0.63 0.01±0.01 4.25±1.80 0.05±0.01 12.20±4.82 0.25±0.04 24 ‘别致’ 79.16±0.49 78.37±0.73 28.92±0.68 31.59±0.62 2.47±0.05 2.34±0.07 1.42±0.03 1.28±0.05 3.92±0.08 3.65±0.12 9.74±0.18 8.77±0.26 25 ‘红星’ 77.48±3.12 60.98±3.64 28.57±0.44 91.04±0.50 1.91±0.04 1.60±0.05 1.07±0.02 0.88±0.03 3.00±0.06 2.50±0.09 7.70±0.16 6.37±0.21 26 ‘变心’ 77.97±2.05 69.19±1.31 51.23±0.81 97.64±0.44 1.70±0.05 1.53±0.03 0.95±0.03 0.85±0.02 2.68±0.08 2.40±0.04 6.69±0.19 6.37±0.12 27 ‘爱莎’ 79.74±0.18 79.21±0.62 32.75±1.67 44.63±0.63 1.86±0.08 1.30±0.03 1.05±0.05 0.72±0.02 2.93±0.13 2.03±0.04 7.43±0.31 4.96±0.11 28 ‘瑞贝卡’ 72.00±2.88 60.55±2.34 29.25±0.29 91.83±0.75 2.44±0.04 2.49±0.07 1.38±0.03 1.44±0.05 3.84±0.07 3.95±0.13 9.63±0.18 9.83±0.35 29 ‘神秘面纱’ 83.19±1.44 74.67±0.94 32.67±0.49 38.33±1.36 2.71±0.08 1.52±0.01 1.53±0.05 0.80±0.01 4.27±0.13 2.34±0.02 10.91±0.37 6.21±0.04 30 ‘努比亚’ 85.31±1.53 78.16±0.88 44.47±0.47 76.90±2.50 3.59±2.60 0.20±0.12 1.66±1.38 0.05±0.04 5.29±4.01 0.24±0.16 14.78±12.48 0.90±0.81 31 ‘薇安’ 77.03±0.57 74.46±0.91 34.39±0.36 38.29±0.36 2.41±0.04 1.30±0.04 1.33±0.02 0.72±0.02 3.77±0.06 2.03±0.07 9.20±0.18 5.23±0.16 32 ‘里昂村庄’ 80.13±0.31 79.51±0.58 30.18±0.83 33.09±0.35 2.41±0.09 2.23±0.04 1.34±0.06 1.24±0.02 3.78±0.15 3.50±0.07 9.58±0.37 9.02±0.17 33 ‘塞拉菲娜’ 80.16±0.34 77.99±0.69 38.24±0.49 48.50±1.00 2.58±0.05 1.91±0.04 1.46±0.03 1.08±0.02 4.07±0.08 3.01±0.06 10.26±0.18 7.46±0.14 34 ‘撒玛利亚’ 78.75±0.13 74.25±0.19 48.54±0.18 60.67±0.60 3.41±0.15 1.99±0.02 1.89±0.07 1.17±0.02 5.34±0.12 3.18±0.04 13.86±0.65 7.76±0.09 35 ‘円空’ 81.01±0.43 77.13±0.23 35.82±0.97 66.36±0.60 2.57±0.07 2.10±0.05 1.44±0.05 1.23±0.03 4.03±0.13 3.35±0.08 9.74±0.29 8.37±0.21 36 ‘钻石球’ 80.37±0.40 73.83±0.27 48.57±1.48 94.17±0.65 1.99±0.03 1.94±0.05 1.06±0.02 1.06±0.03 3.07±0.05 3.03±0.08 8.13±0.13 7.40±0.18 37 ‘哥白尼’ 78.13±0.22 75.84±0.35 59.78±0.76 77.79±0.87 2.41±0.10 1.84±0.08 1.44±0.09 1.04±0.05 3.88±0.19 2.90±0.13 9.47±0.41 7.40±0.31 38 ‘薇尼莎’ 80.03±0.19 77.27±0.19 38.77±0.47 62.81±2.70 2.51±0.04 2.31±0.02 1.39±0.03 1.29±0.01 3.92±0.07 3.63±0.03 9.96±0.13 9.52±0.09 39 ‘哦啦啦’ 79.91±0.23 69.10±0.24 35.60±0.36 83.28±1.35 2.66±0.04 2.27±0.04 1.49±0.03 1.23±0.02 4.18±0.07 3.52±0.06 10.17±0.19 9.06±0.14 40 ‘倪欧碧’ 79.94±0.30 68.97±0.47 34.99±0.69 70.45±0.60 2.33±0.02 2.01±0.03 1.25±0.01 1.05±0.02 3.60±0.03 3.08±0.04 8.79±0.08 7.87±0.10 41 ‘朱莉安’ 74.36±0.21 73.00±0.29 61.06±0.45 78.40±2.56 2.63±0.05 2.00±0.07 1.45±0.03 1.05±0.04 4.11±0.08 3.07±0.11 10.00±0.18 7.67±0.27 42 ‘玛丽玫瑰’ 80.23±0.22 65.84±1.10 50.54±2.24 50.93±0.78 2.19±0.02 2.47±0.03 1.22±0.02 1.36±0.02 3.44±0.04 3.85±0.06 8.58±0.11 10.02±0.14 43 ‘中国红’ 76.24±0.60 70.66±0.49 60.08±0.65 81.67±0.19 2.34±0.10 1.75±0.03 1.36±0.08 0.92±0.02 3.72±0.18 2.68±0.05 9.01±0.45 7.12±0.13 2.3.3 耐涝性指标相关性分析结果
铁线莲耐涝性指标相关性分析结果(表6)表明,叶片的相对含水量、叶色、叶形态、茎色与相对电导率均极显著相关(P<0.01),其相关系数分别为0.604、0.518、0.481、0.394,茎形态与相对电导率显著相关(P<0.05),其相关系数为0.373;叶形态与叶色极显著相关(P<0.01),其相关系数为0.776;茎形态与叶形态极显著相关(P<0.01),其相关系数为0.585,与叶色显著相关(P<0.05),其相关系数为0.377;茎色与叶形态、叶色、茎形态均极显著相关(P<0.01),其相关系数分别为0.697、0.613、0.690;综合评分则与相对电导率、叶色、叶形态、茎色、茎形态均极显著相关(P<0.01)。
表 6 11个指标之间相关性分析Table 6. Correlation analysis among 11 indicators指标 相对电导率 相对含水量 叶绿素a 叶绿素b 总叶绿素 类胡萝卜素 叶形态 叶色 茎形态 茎色 总得分 相对电导率 1 相对含水量 −0.604** 1 叶绿素a −0.102 −0.247 1 叶绿素b −0.109 −0.255 0.994** 1 总叶绿素 −0.106 −0.249 0.999** 0.998** 1 类胡萝卜素 −0.084 −0.254 0.994** 0.989** 0.993** 1 叶形态 −0.518** 0.161 0.189 0.200 0.195 0.169 1 叶色 −0.481** 0.199 0.054 0.058 0.057 0.040 0.776** 1 茎形态 −0.373* 0.065 0.189 0.212 0.198 0.157 0.585** 0.377* 1 茎色 −0.394** 0.079 0.108 0.120 0.113 0.076 0.697** 0.613** 0.690** 1 总得分 −0.524** 0.148 0.167 0.182 0.174 0.138 0.921** 0.807** 0.778** 0.878** 1 注:**表示在 P<0.01水平极显著性相关,*表示在 P<0.05水平显著相关。 2.4 铁线莲园艺品种耐涝等级的确定
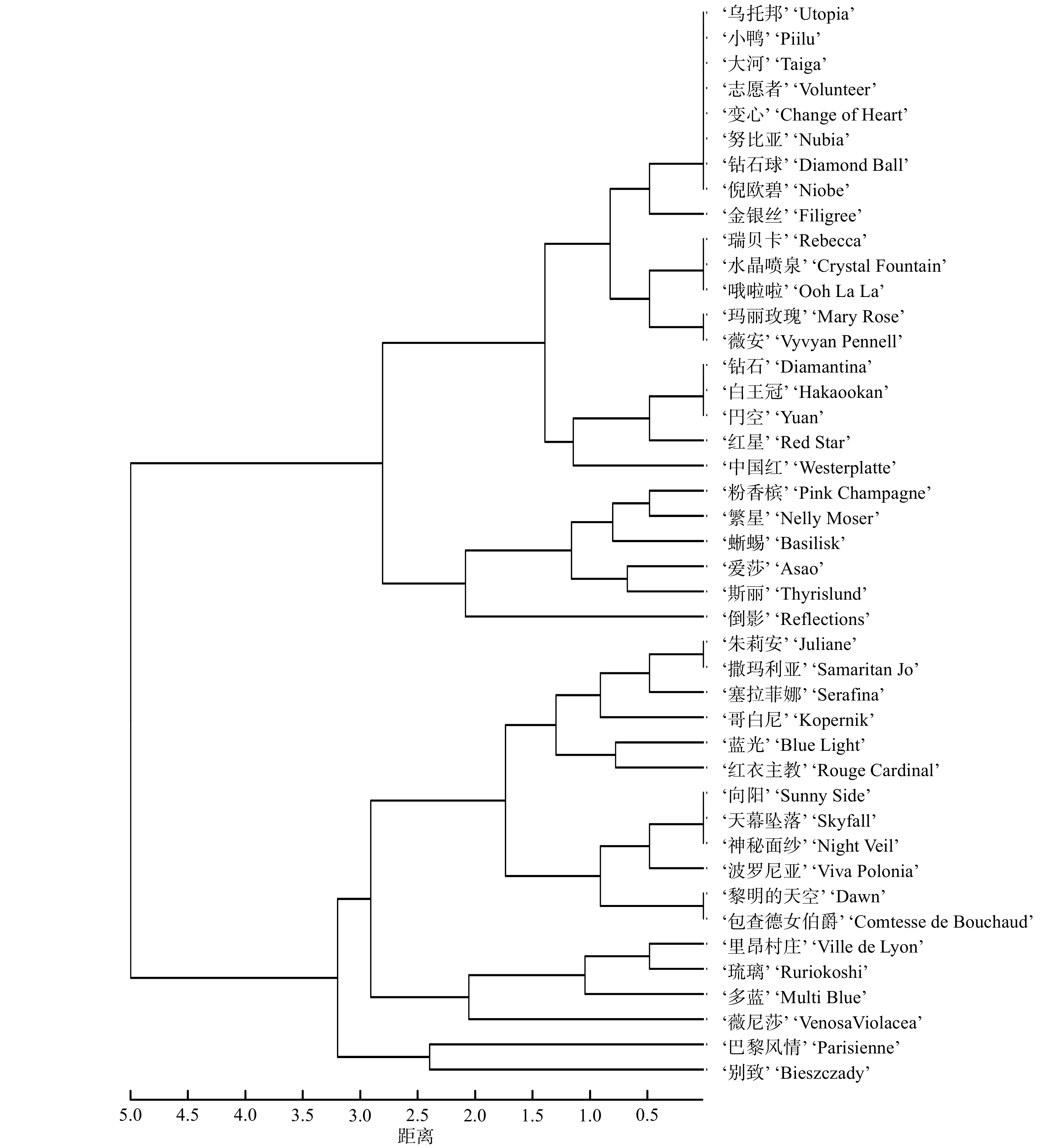
对铁线莲各园艺品种耐涝叶片形态、叶片颜色、茎秆形态、茎秆颜色及生理指标进行聚类分析,结果表明43个铁线莲园艺品种可划分为4类;结合淹水胁迫铁线莲各品种涝害情况,将4类聚类结果分别归为耐涝型、中间型、不耐涝型、极不耐涝型。其中,极不耐涝型品种最多,包括‘小鸭’‘乌托邦’‘大河’‘志愿者’‘变心’‘努比亚’‘钻石球’‘倪欧碧’‘金银丝’‘薇安’‘玛丽玫瑰’‘水晶喷泉’‘红星’‘瑞贝卡’‘哦啦啦’‘白王冠’‘钻石’‘円空’和中国红’共计19个品种;不耐涝型品种包括‘粉香槟’‘爱莎’斯丽’‘繁星’‘蜥蜴’‘倒影’6个品种;中间型品种包括‘薇尼莎’‘琉璃’‘撒玛利亚’‘朱莉安’‘多蓝’‘蓝光’‘波罗尼亚’‘里昂村庄’‘塞拉菲娜’‘哥白尼’‘红衣主教’‘包查德女伯爵’‘黎明的天空’‘天幕坠落’‘向阳’‘神秘面纱’16个品种;‘巴黎风情’与‘别致’ 为耐涝型品种(图1)。
根据涝渍胁迫下铁线莲各园艺品种叶片、茎秆形态指标及相对电导率等生理指标结果,初步建立铁线莲耐涝性评价级别及相应特征(表7),为铁线莲园艺品种的耐涝性判断提供参考。
表 7 铁线莲耐涝性分级评价Table 7. Grading evaluation of Clematis waterlogging tolerance评价等级 分值/分 耐涝性 特征描述 Ⅰ ≥17 耐涝型 植株叶片自然伸展或下层叶片少许萎蔫下垂,叶片绿色或近水处边缘失绿,茎秆正常呈自然色,叶片相对电导率增加10%以下,叶绿素含量降低10%以下 Ⅱ 11~16 中间型 植株中下层叶片萎蔫下垂,黄色或褐色腐烂叶片小于1/3,茎秆正常,颜色呈自然色或浅褐色,叶片相对电导率增加10%~70% Ⅲ 8~10 不耐涝型 植株大部分叶片萎蔫下垂,黄色或褐色腐烂叶1/3至1/2,茎秆形态正常,颜色褐化或发黑,叶片相对电导率增加70%以上 Ⅳ ≤7 极不耐涝型 植株大部分叶片干枯腐烂,黄色或褐色腐烂叶>1/2,颜色褐化或发黑。呈水渍状腐烂,叶片相对电导率增加110%以上 3. 讨论与结论
3.1 涝渍胁迫对铁线莲表型性状的影响
水分是影响植物生长发育的关键因子之一,叶片是植株外部形态对水分胁迫反应最敏感的器官,植物长期处在水分饱和或近饱和状态的土壤环境中,叶片会萎蔫、黄化甚至脱落,因此叶片受害程度可指示植物的耐涝性,与植株的耐涝性呈负相关[9-11]。常见绿化藤本植物中,常春藤Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis、金银花Lonicera japonica、油麻藤Mucuna sempervirens多作为垂直绿化藤本植物,淹水胁迫下这3种藤本均出现失绿表型,相比较而言金银花的耐涝性最强,可通过积累可溶性糖同时提高抗氧化酶活性短期适应水涝胁迫[12]。大麦Hordeum vulgare中涝渍敏感品种‘Franklin’在涝渍胁迫2周后绝大多数叶片变黄,耐涝品种‘Yerong’仅在第1片叶子尖端出现轻微症状[13]。本研究发现,铁线莲受到涝渍胁迫时叶片首先表现出的受害症状为近水处叶片开始萎蔫、黄化,随后逐步扩大至植株中上层叶片,与其他植物在叶片或茎秆表型上受害症状一致[14-15]。极不耐涝品种出现茎秆腐烂黑化,大部分品种茎秆形态未出现水渍化腐烂,仅表现出颜色变为褐色或黑色,这可能与铁线莲茎秆的木质化程度有关。
3.2 涝渍胁迫对铁线莲叶绿素含量及相对电导率的影响
涝渍胁迫抗性评价中常用指标为茎形态、叶形态、根形态、鲜质量、干质量、根系活力、叶绿素含量、相对电导率等形态指标与生理生化参数[16-18],已有研究表明在涝渍胁迫下,植物叶片光合系统被破坏,叶绿素降解相关基因CLH和PaO等上调,叶绿素合成相关基因HEMB、HEMD和HEMF等下调,最终导致叶绿素含量降低、净光合速率降低[19-21]。本研究发现,铁线莲在涝渍胁迫下叶片中的叶绿素含量显著下降,这与蔡进等[22]对2个铁线莲品种对淹水胁迫的生理响应研究结果相一致,其中耐涝型、中间型、不耐涝型与极不耐涝型铁线莲品种叶片中的总叶绿素含量分别平均降低了8.25%、30.45%、28.19%和30.09%,表明耐涝性强的铁线莲品种叶片中的叶绿素合成或降解受涝渍胁迫影响较小,但如何调控则需要进一步深入研究。涝渍胁迫会导致细胞膜透性增加、胞内电解质渗出、相对电导率上升、细胞膜稳定性下降,影响细胞正常的代谢活动[23]。本试验中,涝渍胁迫增加了铁线莲的相对电导率,耐涝型铁线莲品种的相对电导率平均增加了8.58%,中间型铁线莲品种的相对电导率平均增加了32.17%,不耐涝型铁线莲品种的相对电导率平均增加了109.14%,极不耐涝型铁线莲品种的相对电导率平均增加了115.81%,这表明耐涝性强的铁线莲品种具有高度维持细胞膜稳定性的能力,相对电导率是衡量铁线莲品种耐涝性的一个重要指标。
3.3 铁线莲的耐涝性评价
植物可改变呼吸代谢途径、积累渗透调节物质、促进通气组织形成、增强抗氧化酶活性等响应涝渍胁迫[24-25],植物表型是植物生理及分子变化的外在表现,表型的健康状况与植物响应非生物胁迫能力紧密相关[26-27]。尹冬梅等[28]通过4个叶片及茎秆表型指标建立了菊花Dendranthema morifolium 耐涝性评价体系,王俊良等[29]通过对甜瓜Cucumis melo开展耐涝性鉴定,建立了以电导伤害率、萎蔫指数、基部不定根数等为指标的鉴定评价体系。本研究发现,涝渍胁迫下铁线莲各园艺品种叶片叶绿素含量均显著下降,但不同品种叶绿素含量及降低幅度各不相同,相关性分析表明叶绿素含量与耐涝性相关性不显著,这可能是铁线莲品种间遗传背景差异较大导致的,使用叶绿素含量或变化趋势难以区分除极耐涝以外的铁线莲品种,因此仅对耐涝型铁线莲品种做叶绿素含量分级说明。涝渍胁迫下铁线莲相对电导率显著上升,相对电导率与耐涝性相关性显著,其相关系数为0.524,同时表型性状与耐涝性的相关性显著,其相关性由大到小顺序为叶形态>茎色>叶色>茎形态,这说明相对电导率、叶形态、茎色、叶色及茎形态指标可作为耐涝性评价的参考指标。
3.4 铁线莲耐涝性鉴定及应用
本研究将43个铁线莲园艺品种聚类为耐涝型、中间型、不耐涝型和极不耐涝型4种类型。其中,耐涝型有2个品种,中间型有16个品种,不耐涝型有6个品种,极不耐涝型有19个品种。通过对43个铁线莲园艺品种的耐涝性评价,筛选出的耐涝性差的品种可直接确定其不适宜种植环境或区域,为铁线莲耐涝性品种选择提供指导,有效降低管护成本。本研究筛选出的2个耐涝性较强的铁线莲园艺品种(‘巴黎风情’与‘别致’),不仅在抗逆性上表现优异,同时具有极高的观赏价值,对铁线莲高抗逆新品种培育具有重要现实意义。
-
表 1 3种林型土壤理化性质
Table 1 3 forest types of soil physicochemical properties
林型 全氮/
(g·kg−1)全磷/
(g·kg−1)全钾/
(g·kg−1)碱解氮/
(mg·kg−1)有效磷/
(mg·kg−1)速效钾/
(mg·kg−1)有机质/
(g·kg−1)pH值 含水率/
%杉木纯林 4.28±0.45 a 2.14±0.22 a 15.93±0.57 a 159.07±8.80 a 0.81±0.18 b 84.67±8.39 a 108.54±11.35 a 4.48±0.16 a 79.28±5.42 a 毛竹纯林 4.06±0.78 a 1.02±0.20 b 16.07±0.88 a 155.24±25.06 a 1.18±0.04 a 95.00±6.08 a 103.83±19.36 a 4.85±0.29 a 61.98±9.63 b 杉木毛竹混交林 2.75±0.26 b 0.46±0.04 c 15.21±0.34 a 113.72±7.44 b 0.89±0.05 b 58.33±6.11 b 73.15±8.13 b 4.76±0.13 a 61.78±4.10 b 注:表中数据为平均值±标准差(n=3),同一列中不同小写字母表示在0.05水平下具有显著差异(P<0.05);下同。 表 2 3种林型土壤细菌群落α多样性指数
Table 2 Diversity indies for soil bacteria communities in 3 forest types
林型 Shannon 指数 Ace指数 Chao1指数 Simpson指数 Coverage指数 杉木纯林 5.63±0.12b 2 065.97±120.96a 2 056.31±124.53a 0.055±0.005ab 0.993±0.001a 毛竹纯林 5.82±0.05a 2 249.03±30.98a 2 234.87±43.61a 0.055±0.002a 0.993±0.000a 杉木毛竹混交林 5.58±0.10b 2 121.73±123.16a 2 121.62±141.02a 0.047±0.005b 0.993±0.001a 表 3 不同林型土壤细菌优势门、纲和属的相对丰度
Table 3 The relative abundances of dominant bacteria at phylum, class and genus level
林型 门水平下优势细菌的相对丰度/% 酸杆菌门 变形菌门 绿弯菌门 放线菌门 浮霉菌门 RCP2-54 Myxococcota 杉木纯林 (33.23±1.48)a (23.84±2.93)b (16.74±1.63)a (6.08±0.36)b (5.97±0.27)b (3.22±0.12)a (1.60±0.25)ab 毛竹纯林 (28.94±0.94)b (31.51±2.13)a (10.70±1.76)b (8.96±1.52)a (7.59±0.82)a (1.88±0.05)c (2.07±0.40)a 杉木毛竹混交林 (34.05±1.51)a (29.70±3.21)a (12.31±3.56)ab (5.49±0.60)b (6.47±0.84)ab (2.53±0.33)b (1.30±0.24)b 林型 纲水平下优势细菌的相对丰度/% 酸杆菌纲 α-变形菌纲 纤线杆菌纲 浮霉菌纲 γ-变形菌纲 放线菌纲 嗜热油菌纲 Vicinamibacteria 酸微菌纲 杉木纯林 (30.66±1.43)a (18.87±2.06)b (13.47±1.34)a (5.53±0.32)b (4.98±0.89)b (3.19±0.71)b (1.69±0.43)ab (1.31±0.11)a (1.19±0.41)a 毛竹纯林 (25.63±0.95)b (23.55±1.97)a (7.50±1.16)b (7.09±0.82)a (7.95±0.78)a (4.84±0.56)a (2.56±0.69)a (1.66±0.14)a (1.54±0.35)a 杉木毛竹
混交林(31.54±1.08)a (24.39±2.77)a (9.68±3.04)ab (6.03±0.79)ab (5.31±0.47)b (3.09±0.62)b (1.33±0.19)b (1.43±0.29)a (1.04±0.19)a 林型 属水平下优势细菌的相对丰度/% HSB_OF53-F07 热酸菌属 念珠菌固体杆菌属 酸杆菌属 Bryobacter 慢生根瘤菌属 杉木纯林 (5.27±0.33)a (2.36±0.58)a (2.15±0.23)a (2.06±0.47)a (1.18±0.25)a (0.62±0.18)b 毛竹纯林 (2.32±0.49)b (2.60±0.18)a (2.38±0.51)a (2.49±0.30)a (1.12±0.27)a (1.85±0.23)a 杉木毛竹混交林 (3.84±1.41)ab (2.39±0.51)a (2.47±0.57)a (2.10±0.29)a (1.71±0.78)a (1.28±0.47)a -
[1] 陈开伍. 杉木毛竹混交林水源涵养功能的研究[J]. 福建林学院学报,2000,20(3):258 − 261. [2] 郑郁善,王舒凤. 杉木毛竹混交林的毛竹地下鞭根结构特征研究[J]. 林业科学,2000,36(6):69 − 72. [3] 史纪明,张纪林,教忠意,等. 毛竹对杉木林入侵效应初步调查研究[J]. 江苏林业科技,2013,40(1):7 − 9. [4] 童冉,周本智,姜丽娜,等. 毛竹入侵对森林植物和土壤的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2019,39(11):3808 − 3815. [5] 白尚斌,周国模,王懿祥,等. 天目山保护区森林群落植物多样性对毛竹入侵的响应及动态变化[J]. 生物多样性,2013,21(3):288 − 295. [6] KEITO K,KAMEHIRO K,YUSUKE O. A simple method to estimate the rate of the bamboo expansion based on one-time measurement of spatial distribution of culms[J]. Ecological Research,2018,33(6):1137 − 1143. doi: 10.1007/s11284-018-1626-9
[7] XU Q F,JIANG P K,WU J S,et al. Bamboo invasion of native broadleaf forest modified soil microbial communities and diversity[J]. Biological Invasions,2015,17(1):433 − 444. doi: 10.1007/s10530-014-0741-y
[8] 林倩倩,王彬,马元丹,等. 天目山国家级自然保护区毛竹林扩张对生物多样性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2014(9):43 − 47,71. [9] 王奇赞,徐秋芳,姜培坤,等. 天目山毛竹入侵阔叶林后土壤细菌群落16S rDNA V3区片段PCR的DGGE分析[J]. 土壤学报,2009,46(4):662 − 669. [10] 王楠,王传宽,潘小承,等. 模拟酸雨对毛竹入侵阔叶林缓冲区土壤细菌群落多样性的影响[J]. 环境科学研究,2020,33(6):1478 − 1487. [11] 陈珺,张庆晓,顾娇,等. 毛竹入侵对杉木林生长和植被组成的初期影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2021,50(4):517 − 523. [12] BAI S B,WANG Y X,CONANT R T,et al. Can native clonal moso bamboo encroach on adjacent natural forest without human intervention?[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6(6):38269.
[13] 徐道炜,刘金福,何中声,等. 毛竹向杉木林扩张后的群落物种多样性特征[J]. 森林与环境学报,2019,39(1):37 − 41. [14] 李峰,周广胜,曹铭昌. 兴安落叶松地理分布对气候变化响应的模拟[J]. 应用生态学报,2006,17(12):2255 − 2260. [15] 安然,马风云,崔浩然,等. 黄河三角洲刺槐臭椿混交林与纯林土壤细菌群落结构和多样性特征分析. 生态学报,2019,39(21):7960 − 7967. [16] 浦滇,石明,周雪孟,等. 基于高通量绝对定量对不同树龄茶树土壤细菌群落多样性的研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2022,35(1):186 − 193. [17] 张晓,刘世荣,黄永涛,等. 辽东栎林演替过程中的土壤细菌群落结构和多样性变化[J]. 林业科学,2019(10):193 − 202. [18] 纪小芳,龚元,郑翔,等. 凤阳山针阔混交林通量观测源区分布及特征[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(20):7377 − 7388. [19] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000. [20] MAGOČ T,SALZBERG SL. FLASH:fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies[J]. Bioinformatics,2011,27(21):2957 − 2963.
[21] CHEN S,ZHOU Y,CHEN Y,et al. fastp:an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor[J]. Bioinformatics,2018,34(17):i884 − i890.
[22] EDGAR RC. UPARSE:highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads[J]. Nat Methods,2013,10(10):996 − 998.
[23] 李永春,梁雪,李永夫,等. 毛竹入侵阔叶林对土壤真菌群落的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2016,27(2):585 − 592. [24] 范少辉,申景昕,刘广路. 毛竹向杉木林扩展对土壤养分含量及计量比的影响[J]. 西北植物学报,2019,39(8):1455 − 1462. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2019.08.1455 [25] WU J S,JIANG P K,WANG Z L. The effects of phyllostachys pubescens expansion on soil fertility in national nature reserve of Mount Tianmu[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis,2008,30(4):659 − 692.
[26] 蔡亮,张瑞霖,李春福,等. 基于竹鞭状态分析的抑制毛竹林扩散的方法[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2003,31(5):68 − 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2003.05.023 [27] 李伟成,盛海燕,陈伟杰,等. 毛竹入侵马尾松林的土壤菌群多样性变化[J]. 应用生态学报,2018,29(2):3969 − 3976.



 下载:
下载: