Effect of Species Diversity and Stand Structure on the Biomass of Arbor Layer in Forest Dominated by Quercus glauca
-
摘要:
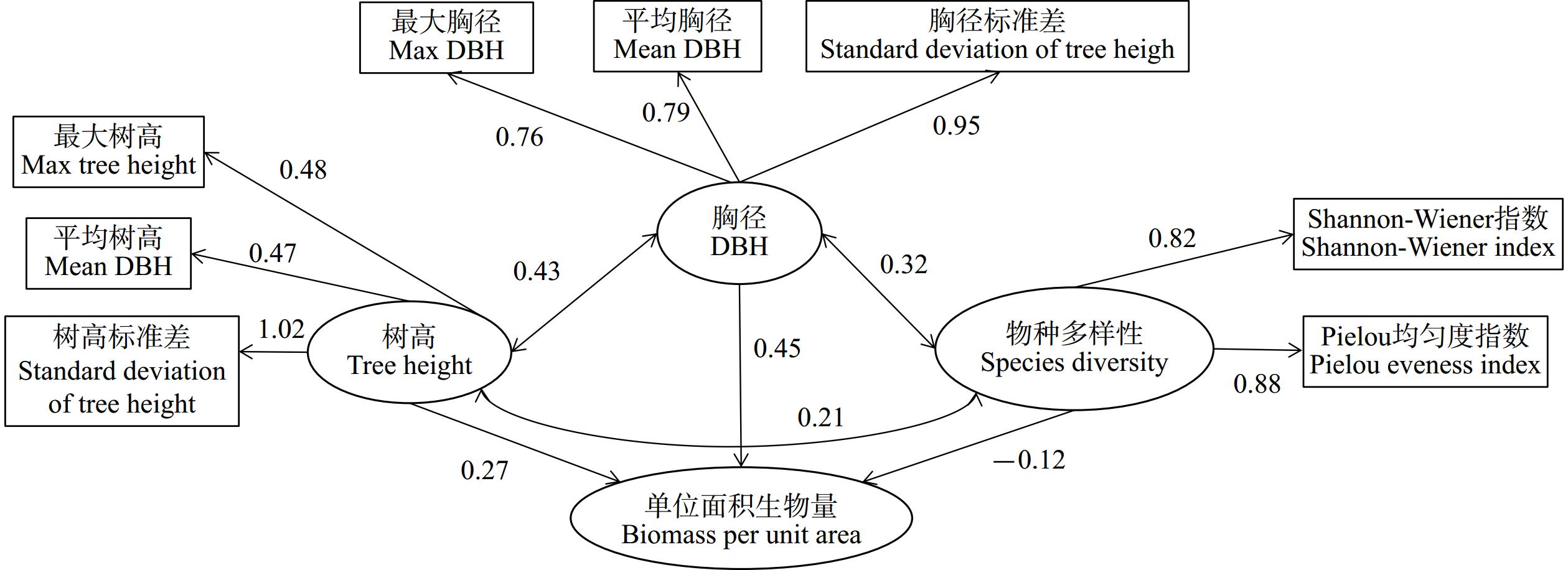
为探究物种多样性和林分结构对青冈Quercus glauca林乔木层生物量的影响,本文以2020年在浙江省9个设区市设置的138个青冈林样地为研究对象,以物种多样性、胸径、树高三个因子作为潜变量,并采用结构方程模型方法,分析了物种多样性、胸径结构和树高结构对青冈林乔木层生物量的影响。结果表明,林木胸径、树高和物种多样性对青冈林乔木层生物量具有直接和间接效应,其直接效应分别为0.17、0.35和−0.42,而通过其他因子产生的间接效应使得总效应分别提高了64.71%、20.00%和40.50%;物种多样性的负效应与青冈林中青冈的主导优势地位有关;异龄复层林经营模式有利于充分利用林内营养空间,促进青冈林生物量的积累。
Abstract:During July and September 2020, 138 sample plots with 20 m×20 m were established in the forest dominated by Quercus glauca in 9 cities of Zhejiang province, and woody plant with DBH ≥5 cm in the plots were recorded. The effect of species diversity, DBH and tree height on biomass of arbor layer was analyzed by structural equation model. The result showed that DBH, tree height and species diversity had direct and indirect effects on the biomass of the canopy layer. The direct effects are 0.17, 0.35, and −0.42, respectively, while the indirect effects through other factors increase the total effects by 64.71%, 20.00%, and 40.50%, respectively. The negative effect of species diversity was related to the dominant position of Qu. glauca.Uneven aged and multi-storied stand forestry management model is beneficial for fully utilizing the nutrient space within the forest and promoting the accumulation of biomass in Qu. glauca forests.
-
Keywords:
- Quercus glauca /
- biomass /
- species diversity /
- DBH /
- tree height
-
-
表 1 样地数量及其分布情况
Table 1 Distribution of sample plots in Zhejiang province
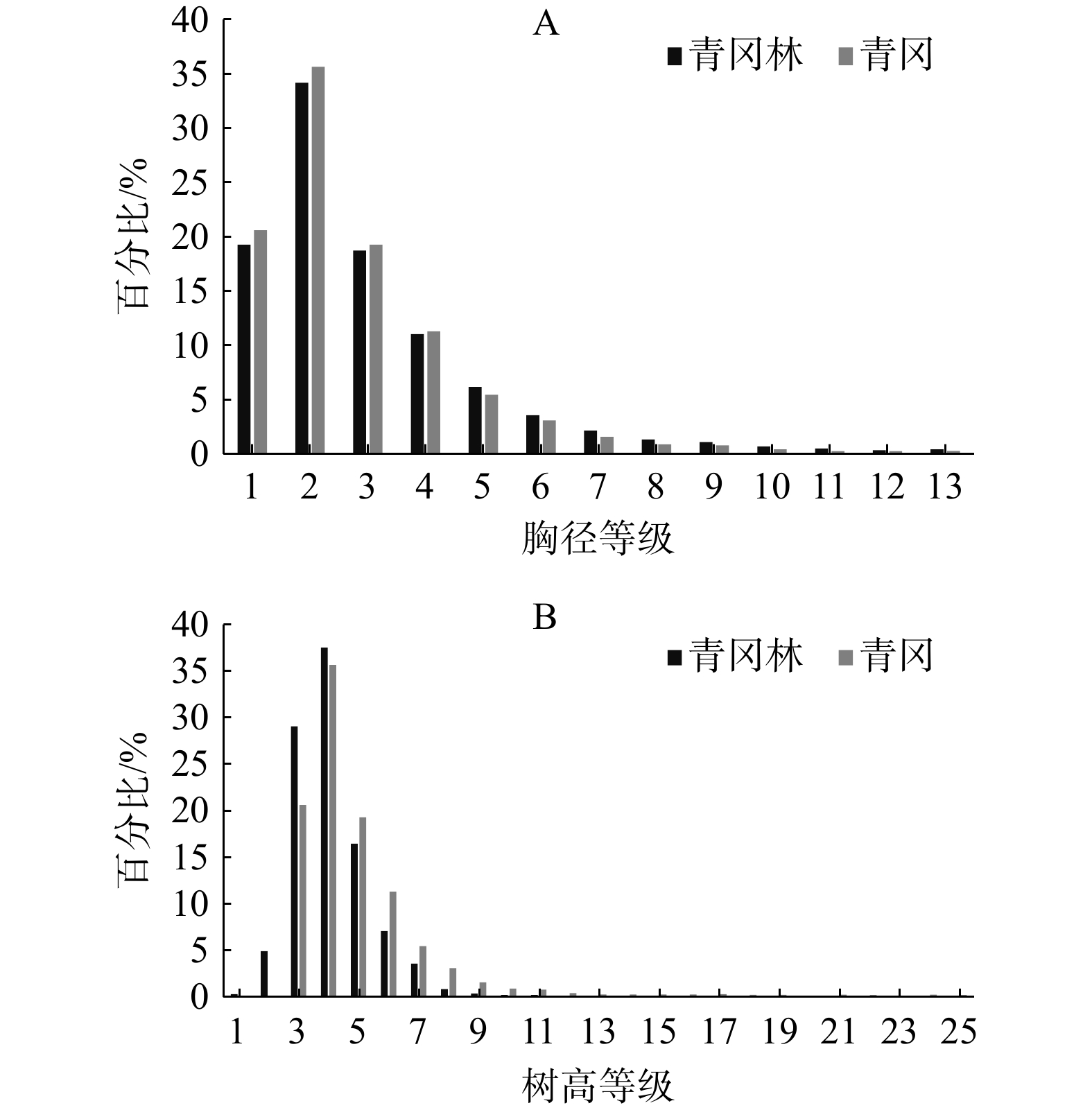
市 县(市、区) 样地数/个 市 县(市、区) 样地数/个 杭州 淳安 13 台州 仙居 10 富阳 5 丽水 景宁 13 建德 10 莲都 7 湖州 吴兴 1 龙泉 31 德清 1 庆元 16 金华 磐安 5 遂昌 18 武义 2 松阳 4 义乌 1 合计 138 舟山 定海 1 表 2 林分结构对青冈林的直接和间接效应系数
Table 2 Coefficient of direct and indirect effect of stand structure on biomass
影响因子 直接效应 间接效应 总效应 林木树高 0.17 0.11 0.28 林木胸径 0.35 0.07 0.42 物种多样性 −0.42 0.17 −0.25 -
[1] 杨远盛,张晓霞,于海艳,等. 中国森林生物量的空间分布及其影响因素[J]. 西南林业大学学报,2015,35(6):45 − 52. [2] 贺金生,方精云,马克平,等. 生物多样性与生态系统生产力:为什么野外观测和受控实验结果不一致?[J]. 植物生态学报,2003,27(6):835 − 843. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2003.06.017 [3] 薛立,杨鹏. 森林生物量研究综述[J]. 福建林学院学报,2004,24(3):283 − 288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-389X.2004.03.021 [4] 倪健,宋永昌. 中国青冈的地理分布与气候的关系[J]. 生态学报,1997,39(5):451 − 460. [5] 李铭红. 40龄青冈林林木层的生物量和净生产量研究[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版),2000,23(2):83 − 86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5051.2000.02.022 [6] 于明坚,陈启瑺. 浙江建德青冈种群结构的研究[J]. 东北林业大学学报,1998,26(5):11 − 16. [7] 于明坚. 青冈常绿阔叶林群落动态研究[J]. 林业科学,1999,35(6):42 − 51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.1999.06.006 [8] 胡小兵,于明坚,陈玉宝. 浙北青冈林群落结构与青冈种群数量特征[J]. 植物研究,2002,22(4):432 − 438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5102.2002.04.011 [9] 李铭红,于明坚,潘文戎. 青冈常绿阔叶林钙的释放动态[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版),2000,27(3):334 − 336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9497.2000.03.019 [10] PIELOU E C. Ecological Diversity[M]. New York. Wiley,1975:16 − 51.
[11] SIMPSON E H. Measurement of diversity[J]. Nature,1949,163(4148):688. doi: 10.1038/163688a0
[12] 袁位高,江波,葛永金,等. 浙江省重点公益林生物量模型研究[J]. 浙江林业科技,2009,29(2):1 − 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3776.2009.02.001 [13] HU L,BENTLER P M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis:Conventional criteria versus new alternatives[J]. Structural Equation Modeling,1999,6(1):1 − 55. doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118
[14] R Core Team. R:A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing(Vienna,Austria. 2002)[EB/OL].[2024-06-20] https://www.R-project.org/.
[15] 陈启瑺,沈琪. 浙江次生青冈林林木层的生物量模型及其分析[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报,1993,17(1):40 − 49. [16] 尉文,庞荣荣,彭潔莹,等. 太白山锐齿栎林地上生物量分布[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2019,41(12):69 − 76. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20190440 [17] 林敦梅,庞梅,赖江山,等. 亚热带常绿阔叶林不同林层物种多样性与地上生物量的多变量关系[J]. 科学通报,2017,62(17):1861 − 1868. [18] 尉海东,马祥庆. 中亚热带不同发育阶段杉木人工林生态系统碳贮量研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2006(2):239 − 243,267. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2006.02.019 [19] ALI A,CHEN H,YOU W,et al. Multiple abiotic and biotic drivers of aboveground biomass shift with forest stratum[J]. Forest Ecology and Management,2019,436:1 − 10.
[20] WEI S,LI L,LIAN J,et al. Role of the dominant species on the distributions of neighbor species in a subtropical forest[J]. Forests,2020,11(3):352. doi: 10.3390/f11030352
[21] YUAN Z,ALI A,SANAEI A,et al. Few large trees,rather than plant diversity and composition,drive the above-ground biomass stock and dynamics of temperate forests in northeast China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2021,481:118698.
[22] LEI X,WANG W,PENG C. Relationships between stand growth and structural diversity in spruce-dominated forests in New Brunswick,Canada[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research,2009,39(10):1835 − 1847. doi: 10.1139/X09-089



 下载:
下载: