Analysis of Secondary Metabolites in Distylium racemosum and Distylium buxifolium Based on Broadly Targeted Metabolomics
-
摘要:目的
挖掘蚊母树Distylium racemosum和小叶蚊母树D. buxifolium药理活性成分,探明小叶蚊母树趋避虫瘿寄生的物质基础。
方法用UHPLC-MS/MS技术对蚊母树和小叶蚊母树进行代谢产物比较,结合多元统计分析方法鉴定差异性成分,并进行差异代谢物HMDB、KEGG通路分析。
结果从蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的代谢产物中共鉴定出15类720种次生代谢产物,其中差异代谢产物有 13类263种,差异较大的是脂质和脂质类化合物、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物,分别占比36.22%和31.53% 。挖掘出具有治疗糖尿病作用的京尼平苷酸和琥珀酸,具有降脂作用的3-羟基甲基苯甲酸、绿原酸和创伤酸,具有心脏保护作用的表儿茶素;高活性的黄酮类物质包括山奈酚、槲皮素、丹叶大黄素,高活性多酚类物质表没食子儿茶素。与小叶蚊母树比较,蚊母树有93种成分上调,170种成分下调,差异代谢物主要显著富集在植物激素生物合成和信号转导、氨基酸生物合成和代谢、苯丙素生物合成、氨酰基-t-RNA生物合成等的代谢通路,小叶蚊母树中高水平的茉莉酸可能是其几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的主要原因。
结论蚊母树和小叶蚊母树化学成分差异较大,但均具有多种已被证明具有明确药理活性的次生代谢产物,具有潜在药用价值可供挖掘。较高水平的茉莉酸可能是小叶蚊母树几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的主要原因之一。
Abstract:In order to investigate the pharmacologically active components of D. racemosum and D. buxifolium, as well as the material basis for D. buxifolium’s resistance to gall parasitism, this study utilized UHPLC-MS/MS technology to compare the metabolites of the two species. Differential components were identified using multivariate statistical analysis, and the pathways of the differential metabolites were analyzed using HMDB and KEGG databases. The results identified a total of 720 secondary metabolites across 15 categories in D. racemosum and D. buxifolium. Among these, 263 differential metabolites were identified in 13 categories, with lipids and lipid-like molecules (36.22%) and phenylpropanoids and polyketides (31.53%) showing the most significant differences. Key metabolites were identified, including geniposidic acid and succinic acid, which have antidiabetic properties; 3-hydroxymethylbenzoic acid, chlorogenic acid, and traumatic acid, which contribute to lipid reduction; and epicatechin, which has cardioprotective effects and the ability to inhibit liver fibrosis. Furthermore, highly active flavonoids such as kaempferol, quercetin, and salvia emodin, as well as the polyphenol epigallocatechin, were identified, providing valuable insights for the medicinal development of D. racemosum and D. buxifolium. Compared to D. buxifolium, D. racemosum exhibited 93 upregulated and 170 downregulated components. The differential metabolites were primarily enriched in metabolic pathways related to plant hormone biosynthesis and signal transduction, amino acid biosynthesis and metabolism, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis. Notably, the high levels of jasmonic acid in D. buxifolium may be the key factor explaining its resistance to gall parasitism.
-
金缕梅科Hamamelidaceae植物具有极高的观赏和药用价值,其中蚊母树Distylium racemosum和小叶蚊母树D. buxifolium 具有良好的耐荫性和耐强光性,对生长环境适应性强,是优良的园林地被植物。目前,针对蚊母树属Distylium植物的研究多集中在虫瘿类型、扦插繁殖、光合特性和水淹胁迫、成分研究、虫害防治等方面[1-7]。现有药理研究表明,蚊母树属植物具有抗菌、抗癌、抗炎、抗病毒和抗肥胖的作用[8-12],如中华蚊母树根中的内生真菌具有广谱抗菌和抗癌活性[9];蚊母树提取物对过敏性哮喘小鼠具有抗炎活性[10]; Kim等[11-12]研究表明蚊母树乙酸乙酯部中槲皮素对人腺病毒36的增殖有抑制作用,或对体外脂质积累具有抑制作用,可作为肥胖治疗剂的材料来源。可见,对于蚊母树属植物的药理活性及其活性成分的研究刚刚起步,多为对某组分药理活性的研究,对于活性成分及其发挥作用的确切机制仍有待进一步阐明。故本研究选用蚊母树及小叶蚊母树两种蚊母树属植物,基于广泛靶向代谢组学的研究,对其中含量较高、具药理活性的次生代谢产物进行分析汇总,为挖掘蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的潜在药用价值及进一步活性验证提供一定参考。
蚊母树属植物叶片上经常出现绿色、黄绿色或紫红色的虫瘿,5月中旬虫瘿破裂,迁移蚜飞出,虫瘿开口处开始变黑直至干枯坏死,其中蚊母树受害尤为严重,而小叶蚊母树几乎不受危害[11-12]。蚊母新胸蚜Neothoracaphis yanonis的防治通常通过修剪和药剂防治,但对致瘿昆虫的防治往往比较困难,而小叶蚊母树因几乎不受虫瘿困扰是研究防治虫瘿虫害的优异材料,但其化学成分基础目前尚少有人研究。张敏等[12]对蚊母树和小叶蚊母树嫩叶挥发性成分的检测结果显示,顺式-3-乙烯醇(又叫叶醇,C6H12O)分别占两者总挥发物的68.12%和10.31%,推测其在蚊母新胸蚜寄主选择中发挥了重要作用,但对小叶蚊母树趋避新胸蚜寄生的物质基础未有结论。本研究基于广泛靶向代谢组学,通过对比蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的差异代谢产物,并对其富集的主要代谢通路及其功能进行分析,揭示小叶蚊母树几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的原因,为蚊母树虫瘿防治提供新的思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 仪器
BSA124S-CW天平(Sartorius);D24 UV纯水仪(Merck,illipore);JXFSTPRP-24组织破碎仪(净信);T3 column(100 mm*2.1 mm,1.8 μm)(Waters);Vanquish Flex UHPLC-MS/MS(Thermo)。
1.1.2 材料
实验用蚊母树(WMS-Dr)和小叶蚊母树(WMS-Db)测试材料均采自丽水市莲都区白口小叶蚊母种质资源收集基地。2023年5月,采收蚊母树和小叶蚊母树各6个植株的新鲜叶片数枚,冷冻干燥后,−80 ℃保存备用。实验用试剂有甲醇、乙腈、甲酸(色谱纯,美国Fisher公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 检测条件
1.2.1.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:ACQUITY UPLC T3 C18(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 µm,Waters,Milford,USA);流动相:A水(0.1%甲酸)-B乙腈(0.1%甲酸),洗脱梯度(0~0.5 min,5% B;0.5~7 min,5%~100% B;7~8 min,100% B;8~8.1 min,100%~5% B;8.1~10 min,5% B);流速:0.4 mL·min−1;柱温:35 ℃;进样量:5 μL。
1.2.1.2 质谱条件
采用正、负离子两种检测模式,质量扫描范围(70~
1050 ) m/z,雾化气体为高纯度氮气(N2),电喷雾离子源(ESI)参数:ESI(±),4 500 V;雾化气体(GS1)为50 psi,加热气体(GS2)为60 psi,帘式气体(CUR)为25 psi,加热器温度(TEM)为 550 ℃。1.2.2 样品制备
将蚊母树(Dr)和小叶蚊母树(Db)2组样品真空冷冻干燥后,液氮下研碎,混合均匀, 分别取Dr 和Db样品6个,共12个样品。分别称取100 mg组织样品,进行液氮研磨,加入120 μL 50%甲醇,震荡充分混匀,提取样品中的代谢物,常温静置 10 min。提取液−20 ℃ 过夜,沉淀样品中的蛋白质。转速4 000 g 离心 20 min,0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤并转移上清液代谢物提取液到 96 孔板,每个样品等量取出 10 μL 稀释液混合成质控样品(quality control,QC ),−80 ℃保存。对所提取的样本进行随机上机排序检测,在样品前、中、后部分别插入一个QC样品作为实验技术重复评估。
1.3 数据处理
对质谱下机原始数据利用Proteowizard的MSConvert软件转换成可读数据mzXML。利用XCMS软件进行峰提取,并做峰提取质控。对提取到的物质利用CAMERA进行代谢物同位素、加和离子注释分析,利用metaX软件结合HMDB、KEGG等公共数据库进行一级鉴定,候选鉴定物质分别利用HMDB、KEGG等数据库进行代谢物注释,解释代谢物的物理化学性质、生物功能。对校正后的数据进行过滤,即将所有QC样品中变异系数(CV)>30%的离子过滤掉(CV>30%的离子在实验过程中波动较大,不做差异定量分析)。二级质谱信息与in-house 代谢物标准品数据库进行匹配。利用metaX软件对差异代谢物进行定量、差异代谢物筛选,差异离子同时满足:(1)ratio (表达差异倍数)≥1.5 或 ratio≤1/1.5;(2)P值<0.05;(3)变量重要性投影(variable importance in project, VIP )≥1,进行主成分分析(PCA)、聚类热图分析、偏最小二乘法判别分析(PLS-DA),并进行差异代谢物的HMDB、KEGG通路富集分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蚊母树与小叶蚊母树的代谢成分总体分析
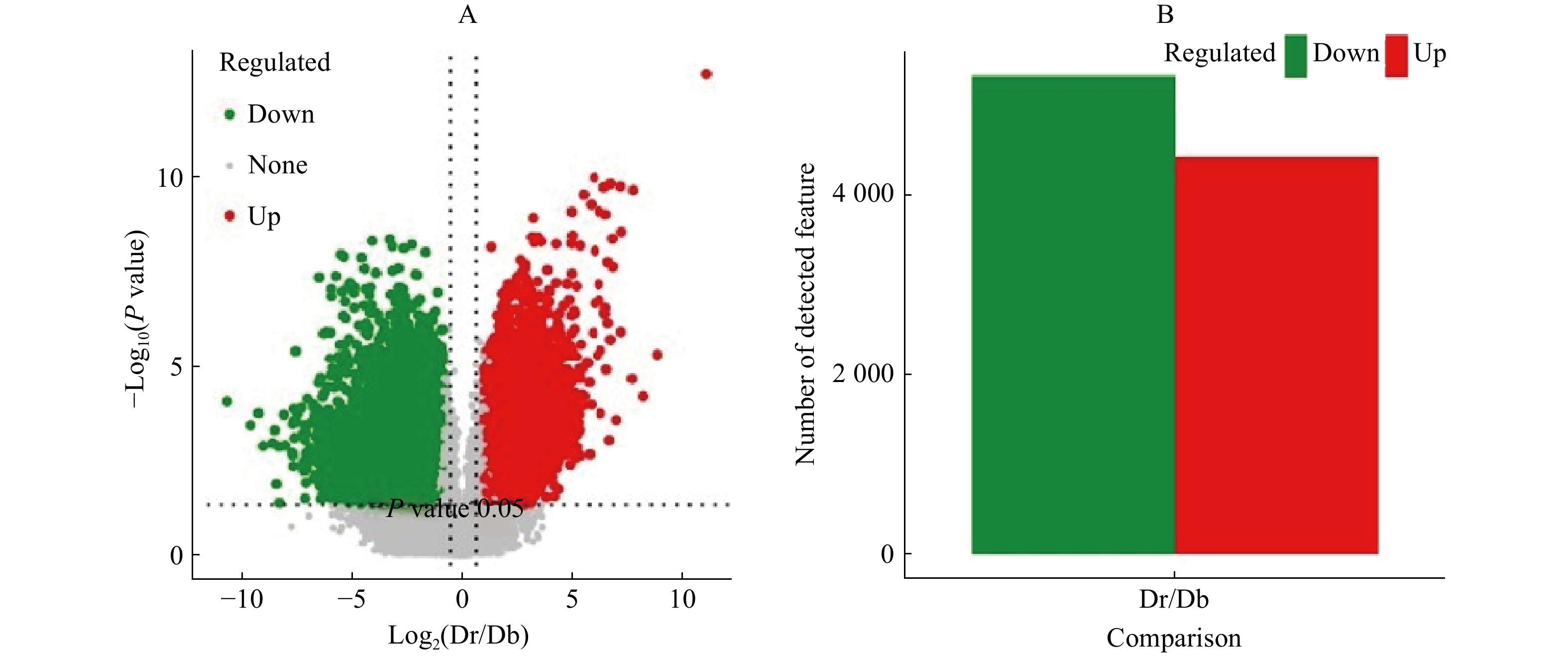
根据PLS-DA模型的变量重要性投影(VIP)鉴定差异代谢物,标准为VIP≥1和ratio≥1.5 或ratio≤1/1.5,P<0.05,即代谢物在对照组和实验组中差异为1.5倍以上或1/1.5以下,当ratio≥1.5表示差异上调,ratio≤1/1.5则表示差异下调。利用火山图展示差异代谢物(单变量统计检验),以代谢离子在比较组中的差异倍数为横坐标, -Log10(q-value)为纵坐标进行展示。蚊母树较小叶蚊母树共有5 336种代谢物下调,4 437种代谢物上调,说明两者间存在显著差异,见图1。
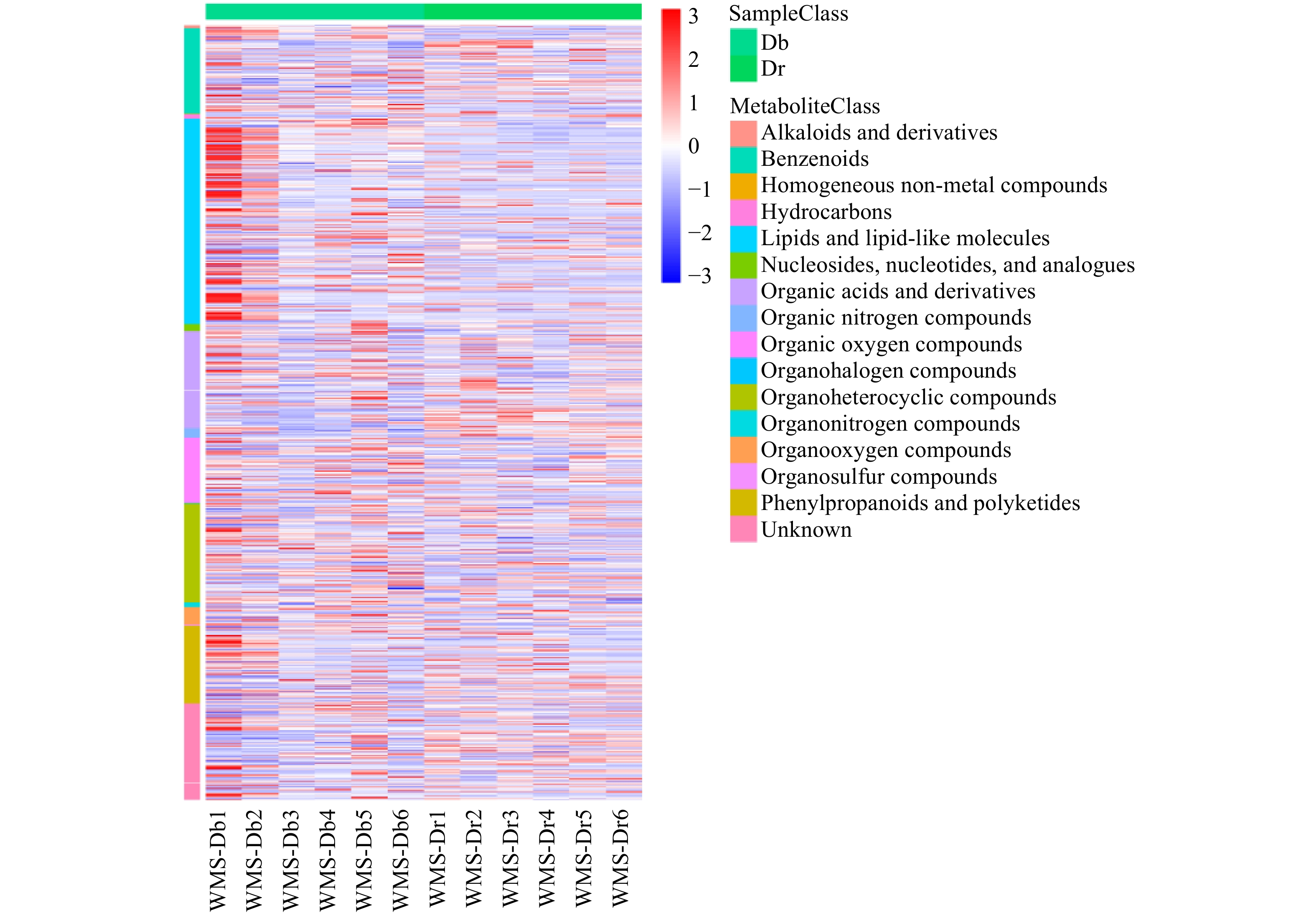
基于联川in-house数据库及HMDB、KEGG代谢物信息公共数据库,在蚊母树和小叶蚊母树中共注释15类720个代谢物,分别为脂质和脂质样分子(162个)、有机酸及其衍生物(96个)、有机杂环化合物(89个)、苯环类化合物(84个)、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物(83个)、有机氧化合物(65个)、含氧有机化合物(16个)、有机氮化合物(7个)、核苷、核苷酸和类似物(7个)、含氮有机化合物(5个)、碳氢化合物(5个)、生物碱及其衍生物(4个),有机硫化合物、均质非金属化合物和有机卤素化合物各1个,其他94个。其代谢产物热点图见图2。
2.2 蚊母树与小叶蚊母树差异代谢组学分析
2.2.1 PCA分析结果
通过对样本鉴定到的代谢离子进行PCA分析,将蚊母树组和小叶蚊母树组分别聚为一组,提示组内重复性佳,2组在PCA二维图上存在明显的分离,提示样品组间代谢组存在差异。选取2个主成分累积贡献率达到64.11%,其中PCA1、PCA2的贡献率分别为42.33%、21.78%。PCA二维得分图和2个主成分贡献率见图3。
2.2.2 PLS-DA分析结果
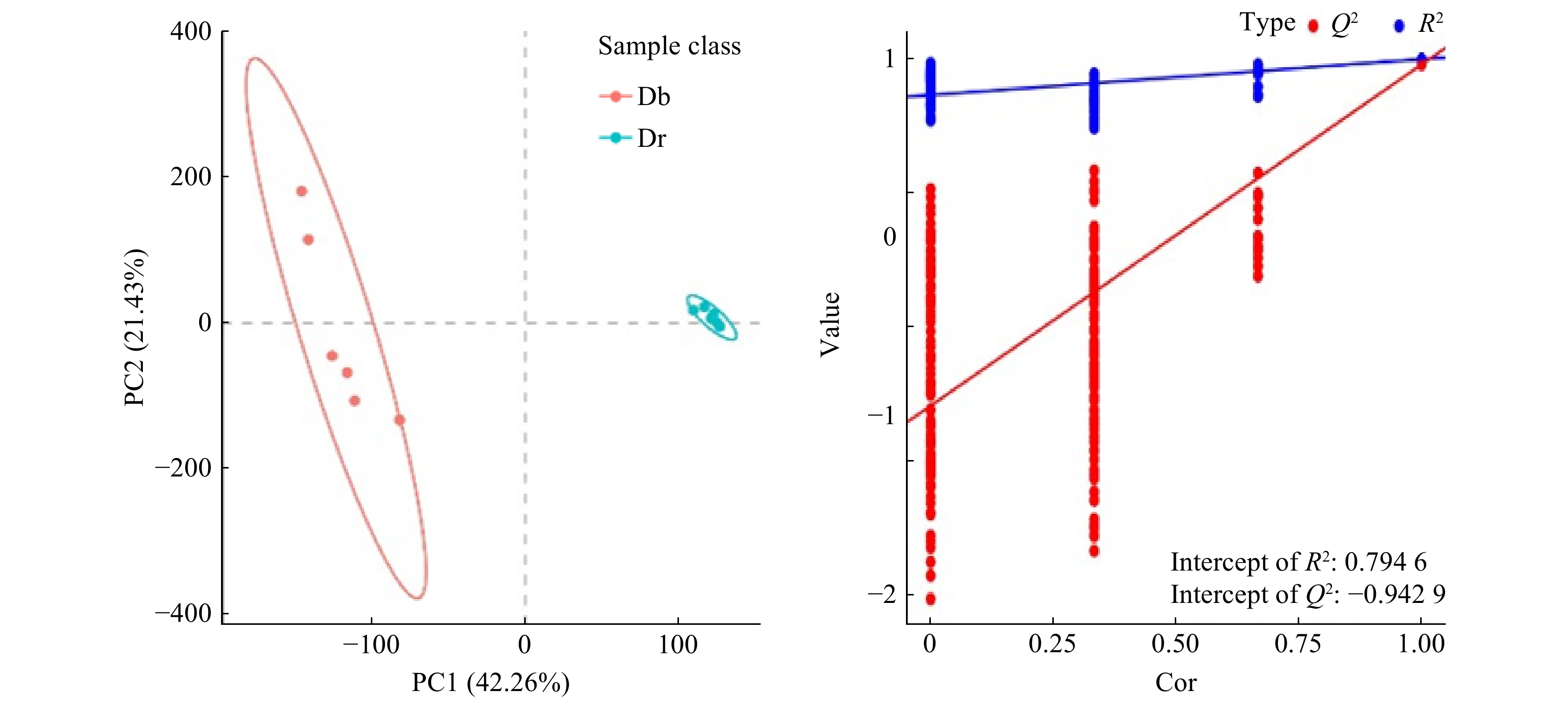
为了最大限度地减少组内无关变量干扰、最大程度地反映不同组别之间的差异,运用偏最小二乘回归建立代谢物表达量和样品类别之间的PLS-DA模型,通过计算变量重要性投影(VIP)辅助代谢物的筛选(以VIP≥1.0作为筛选条件),同时对该模型参数R2和Q2进行置换检验,检验次数为200次。建立每两个组之间的PLS-DA模型,结果显示,2组样本PLS-DA分布有明显区分,无任何重叠,见图4A。模型参数R2(模型解释率)=0.794 9, Q2(模型预测率)=−0.942 9,表明拟合模型的准确度和预测能力稳定可靠。
2.2.3 差异代谢产物分析结果
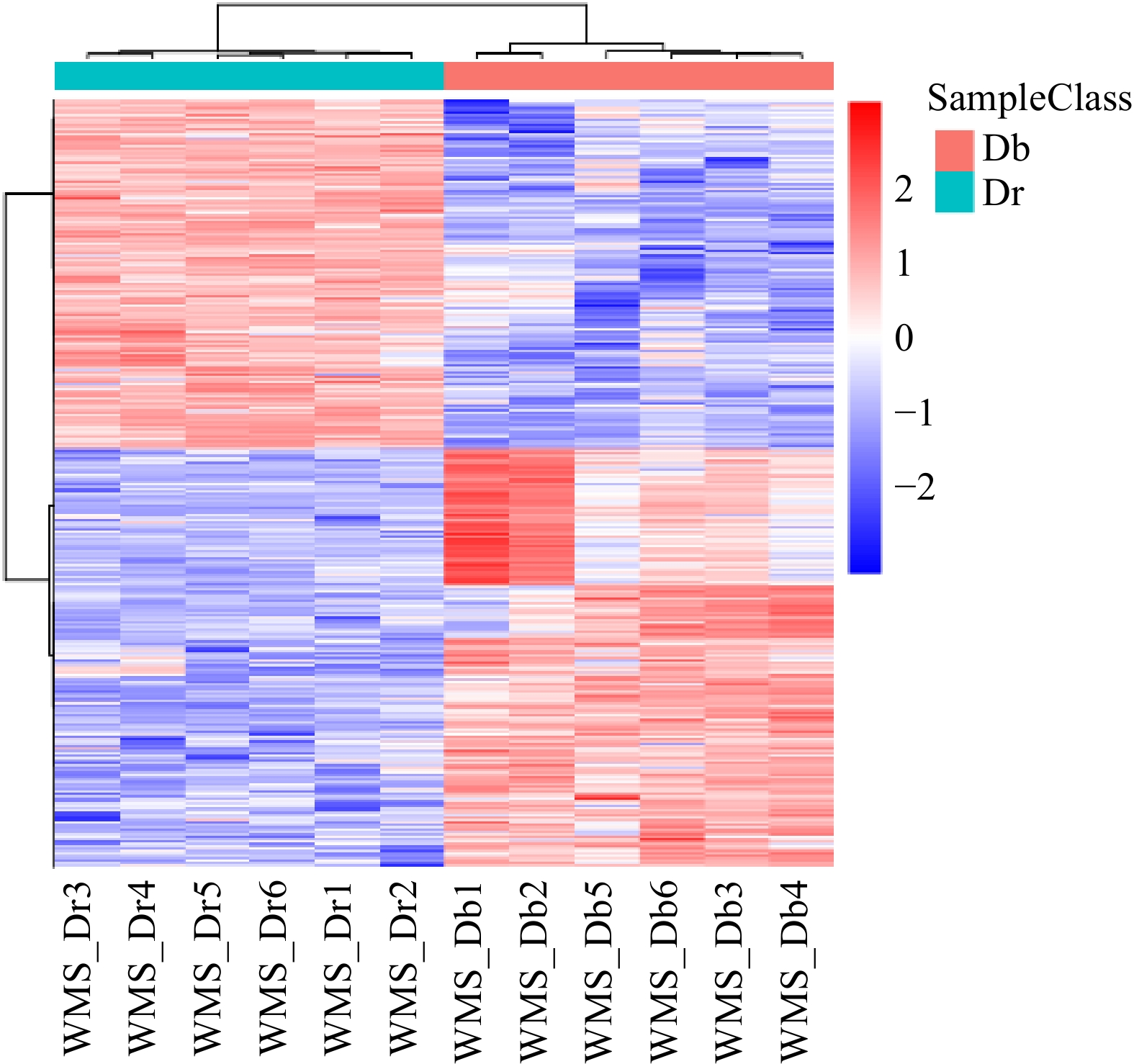
基于联川in-house数据库及HMDB、KEGG代谢物信息公共数据库,蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的二级质谱共注释差异代谢产物263种,其中170个差异代谢产物下调,93个差异代谢产物上调,其差异代谢产物积累热图见图5。
对小叶蚊母树和蚊母树差异代谢产物相对含量进行统计,将任一方中相对含量大于0.5%的次生代谢产物进行汇总,结果见表1。由表1可知,蚊母树和小叶蚊母树次生代谢产物的覆盖率分别为80.40%和83.39%。其中差异较大的是脂质和脂质分子、苯丙烷类和聚酮类、苯环型化合物、有机杂环化合物和有机酸及其衍生物,分别占比9.03%、4.72%、4.58%、4.58%和4.17%。其中,挖掘出多个已有研究表明具有药理活性的成分,将其相对含量(Db、Dr)结果汇总如下:可用于治疗糖尿病[13-14]的京尼平苷酸(0.32%、1.78%)和琥珀酸(2.09%、0.85%),可降脂[11-12, 15-16]的3-羟基甲基苯甲酸(2.18%、1.71%)、绿原酸(5.38%、1.14%)和创伤酸(2.83%、0.12%),具有心脏保护和抑制肝纤维化作用[17-18]的表儿茶素(6.17%、1.26%),高活性的黄酮类物质[19-20]山奈酚(0.85%、6.76%)、槲皮素(0.68%、2.96%)、丹叶大黄素(4.44%、1.30%),高活性多酚类物质表没食子儿茶素[21](1.37%、0.83%),用于治疗小儿急性淋巴细胞白血病[22]的6-巯基嘌呤(0.23%、3.27%)及L-苯丙氨酸(0.89%、5.71%)、L-色氨酸(0.31%、1.85%)、L-精氨酸(0.20%、2.95%)等氨基酸,为小叶蚊母树和蚊母树的潜在药效挖掘提供多个较为准确的方向指引。
表 1 小叶蚊母树和蚊母树差异代谢产物相对含量(≥0.5%)统计Table 1. Statistical table of relative content of differential metabolites (≥0.5%) in D. racemosum and D. buxifoliumID 代谢物名称 相对含量
(Db)/%相对含量
(Dr)/%含量比值
(Dr/Db)ratio VIP 类型 pos-M175T253 alpha-Ionene 0.11 1.21 11.13 6.84 1.82 up neg-M169T73 没食子酸 2.04 12.70 6.23 4.11 1.50 up pos-M111T258 2,4-辛二烯 0.00 0.46 186.60 114.80 2.79 up pos-M129T258 (R)-Sulcatol 0.01 0.53 91.90 56.54 2.57 up neg-M373T221 京尼平苷酸 0.32 1.78 5.55 3.42 1.30 up pos-M145T263 2-甲基庚酸 1.64 5.93 3.61 2.22 1.08 up pos-M180T64 3-羟基甲基苯甲酸 2.18 1.71 0.79 0.48 1.03 down neg-M293T425 (9Z,12Z,14E)-16-Hydroxy-9,12,14-octadecatrienoic acid 0.49 0.14 0.28 0.17 1.36 down neg-M293T401 9-HOTrE 2.36 0.64 0.27 0.17 1.23 down pos-M275T413 诺龙 0.49 0.08 0.16 0.15 1.36 down pos-M291T323 (9Z,11E,13E,15Z)-4-Oxo-9,11,13,15-octadecatetraenoic acid 0.79 0.08 0.10 0.08 1.43 down neg-M225T290 3,4-Methylenesebacic acid 1.97 0.15 0.07 0.05 2.01 down neg-M227T276 愈伤酸 2.83 0.12 0.04 0.03 2.10 down neg-M209T276 茉莉酸 2.51 0.20 0.08 0.03 2.17 down neg-M211T337 Traumatin 1.03 0.04 0.04 0.03 2.00 down neg-M323T332 Cibaric acid 0.95 0.03 0.03 0.02 2.22 down neg-M291T392 (2'E,4'Z,7'Z,8E)-Colnelenic acid 4.14 0.17 0.04 0.01 2.09 down neg-M307T349 Corchorifatty acid D 2.59 0.13 0.05 0.01 2.13 down pos-M130T79 2-哌啶甲酸 0.08 0.95 12.67 11.30 1.92 up pos-M175T43 L-精氨酸 0.20 2.95 14.78 9.09 1.88 up pos-M166T182 L-苯丙氨酸 0.89 5.71 6.41 3.94 1.51 up pos-M132T103 异亮氨酸 0.65 3.05 4.69 2.88 1.23 up neg-M133T43 D-(+)-苹果酸 3.64 2.57 0.70 0.44 1.12 down neg-M191T188 D-(-)-奎宁酸 2.80 1.62 0.58 0.36 1.24 down neg-M117T57 琥珀酸 2.09 0.85 0.41 0.25 1.53 down pos-M184T64 磷酸胆碱 0.26 0.99 3.78 5.50 1.64 up pos-M289T188 Phlorin 0.53 1.75 3.33 2.05 1.05 up neg-M402T195 2,4-Dihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-
one 2-glucoside0.03 2.28 66.35 40.82 2.49 up neg-M179T261 表肌醇 0.03 0.79 24.03 14.78 2.10 up neg-M415T218 2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde O-[xylosyl-(1->6)-glucoside] 0.13 0.90 6.91 4.25 1.47 up pos-M261T38 D-肌醇-4-磷酸 0.56 0.47 0.85 0.52 1.02 down neg-M353T200 绿原酸 5.38 1.14 0.21 0.13 1.85 down neg-M207T291 (Z)-3-Oxo-2-(2-pentenyl)-1-cyclopenteneacetic acid 0.68 0.06 0.09 0.04 2.06 down pos-M153T217 6-巯基嘌呤 0.23 3.27 14.34 3.97 1.35 up pos-M188T200 3-吲哚丙烯酸 0.48 2.88 6.05 3.72 1.49 up pos-M205T200 L-色氨酸 0.31 1.85 5.94 3.66 1.47 up pos-M86T103 六氢吡啶 0.21 0.90 4.34 2.67 1.16 up pos-M85T64 呋喃酮 A 0.79 0.59 0.75 0.46 1.05 down neg-M243T382 枇杷呋喃 4.00 2.41 0.60 0.37 1.53 down neg-M111T43 糠酸 0.60 0.35 0.58 0.36 1.18 down neg-M143T49 2-甲基-5-甲硫基噻吩 0.33 0.21 0.62 0.38 1.27 down pos-M287T257 山奈酚 0.85 6.76 7.99 4.91 1.63 up pos-M303T247 槲皮素 0.68 2.96 4.38 2.69 1.29 up neg-M305T210 表没食子儿茶素 1.37 0.83 0.60 0.37 1.15 down pos-M163T190 3-羟基香豆素 3.26 1.12 0.34 0.21 1.52 down neg-M257T351 丹叶大黄素 4.44 1.30 0.29 0.18 1.79 down neg-M289T219 表儿茶素 6.17 1.26 0.20 0.13 1.84 down pos-M287T332 橡精 0.11 0.84 7.47 7.88 1.88 up neg-M403T219 Oleoside 11-methyl ester 0.22 0.99 4.43 2.15 1.07 up neg-M309T379 9-Oxo-11-(3-pentyl-2-oxiranyl)-10E-undecenoic acid 11.54 0.52 0.05 0.03 2.09 down 基于小叶蚊母树和蚊母树实际虫瘿寄生情况的显著差异,认为蚊母树较小叶蚊母树差异代谢产物相对含量下调物质中可能存在显著驱逐虫瘿寄生的活性成分,如小叶蚊母树中Cibaric acid 、Traumatin、(2'E,4'Z,7'Z,8E)-Colnelenic acid、愈伤酸、9-Oxo-11-(3-pentyl-2-oxiranyl)-10E-undecenoic acid含量分别为蚊母树的31.67、 25.75、24.35、23.58、22.19倍;而显著上调物质中可能存在吸引虫瘿寄生的活性成分,如2,4-辛二烯、(R)-Sulcatol、2,4-Dihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one 2-glucoside 、表肌醇含量分别为小叶蚊母树的186.60、91.90、66.35、24.03倍。已有研究中尚无表明上述物质具有吸引或驱避蚜虫寄生的相关研究结果,所以无法给出确切结论,仍需进一步实验研究加以验证。
2.3 差异代谢产物通路分析
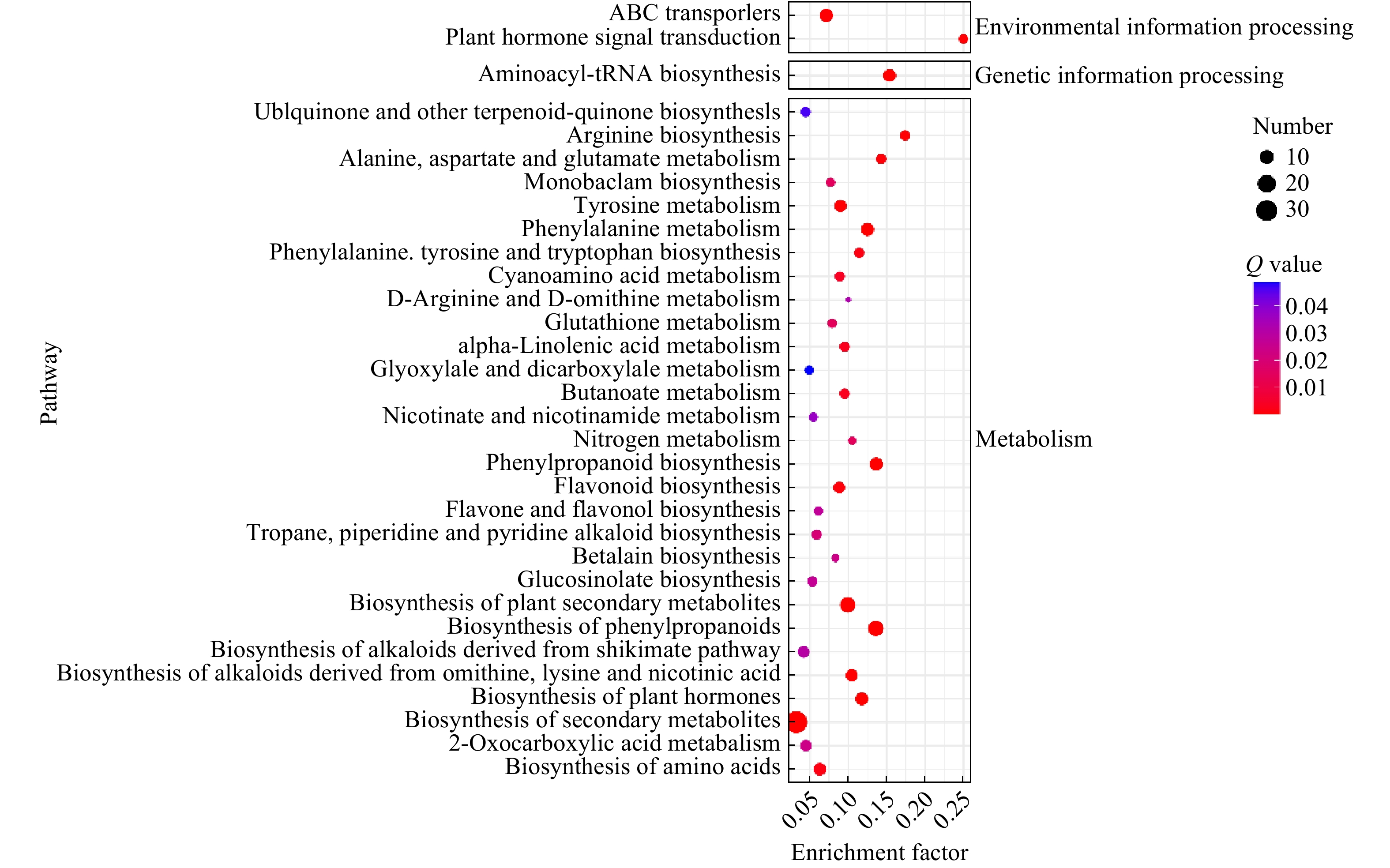
对差异代谢产物进行通路富集分析有助于了解其代谢途径的变化机制,利用KEGG数据库对检测到的差异代谢产物进行注释并进行通路富集分析。筛选出的差异代谢产物共富集在77条代谢通路上,Top32富集通路见图6。其中差异最显著的前8条通路依次为植物激素信号转导,精氨酸生物合成,氨酰基-tRNA生物合成,丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢,植物激素的生物合成,苯丙素的生物合成,苯丙氨酸代谢和苯丙烷类化合物的生物合成。可见,蚊母树和小叶蚊母树主要差异代谢产物集中在氨基酸合成和代谢上,植物激素信号转导及苯丙烷生物合成等次之,且后两者均与植物抗性息息相关[23]。
以上研究结果表明,差异最显著的差异代谢产物为植物激素信号转导,表明激素可激发植物基因的表达,在植物信息处理方面作为信号分子诱导植物的化学防御以增强植物抗性,结合“2.2”项下,本研究发现,小叶蚊母树较蚊母树中茉莉酸含量显著上调12.68倍。茉莉酸是植物主要抗性相关激素信号途径,对生物和非生物胁迫可作出快速反应。研究表明,在应对生物和非生物胁迫如抗虫、抗病、干旱、温度、盐和重金属、抗真菌等方面发挥重要作用,可通过诱导蛋白酶抑制剂和多酚氧化酶从而影响植食性动物对营养物质的吸收,还能通过增加过氧化物酶、壳聚糖酶和脂氧合酶等防御蛋白的活性水平导致生物碱和酚酸类次生物质的积累,增加并改变挥发性信号化合物的释放,甚至形成毛状体和树脂导管等防御结构,产生与昆虫取食相似的效果,进而正向调控植物的抗虫性[24] ;其下游产物包括创伤素、创伤酸、茉莉酸盐和茉莉酸甲酯等,可促进植物伤口愈合,阻止病原体进一步入侵,在植物防御过程中起着关键作用[25-31]。推测高水平茉莉酸可能是小叶蚊母树几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的主要原因之一[32]。
3. 讨论与结论
植物代谢组学具有“高维、海量”的特点,结合多元统计分析方法可以多维度揭示植物体对环境响应下的代谢产物变化模式,对于挖掘植物中的活性成分及其潜在药用价值有重要意义。采用UHPLC-MS技术对蚊母树及小叶蚊母树次生代谢产物进行比较,共鉴定出15类720种次生代谢产物,其中差异代谢产物共13类263种,其中差异较大的是脂质和脂质类化合物、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物,分别占比36.22%和31.53% 。与小叶蚊母树相比,蚊母树中有93种成分上调,170种成分下调,差异代谢产物主要显著富集在植物激素生物合成和信号转导、氨基酸生物合成和代谢、苯丙素生物合成、氨酰基-t-RNA生物合成等的代谢通路。其中涉及大量的氨基酸生物合成和代谢通路,其中色氨酸、苯丙氨酸为必需氨基酸,此外,还包括精氨酸、酪氨酸和谷氨酰胺。巨云为等[33]研究表明,蚊母树在遭到新胸蚜取食后,启动了一系列生理生化响应机制,包括叶片相对电导率、MDA含量、蛋白质含量和SOD活性显著升高,其中虫瘿形成初期瘿边叶蛋白质含量显著升高,形成后期叶片各部分蛋白质均显著升高。蚊母树和小叶蚊母树受虫瘿寄生危害程度的显著差异,可能是导致其氨基酸合成和代谢显著差异的主要原因。
本研究基于广泛靶向代谢组学,从蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的共性成分中挖掘出多个药理活性成分,如用于治疗糖尿病的次生代谢产物京尼平苷酸和琥珀酸[13-14],与样本在KEGG分泌和代谢疾病——AGE-RAGE信号通路在糖尿病并发症上聚集相印证。具有降脂作用的京尼平苷酸、3-羟基甲基苯甲酸[15]、绿原酸和创伤酸,与已有研究蚊母树叶片乙酸乙酯提取物呈剂量依赖型发挥抗肥胖作用[5]相印证。现代药理表明,3-羟基甲基苯甲酸主要通过对羟甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶的抑制作用起到降脂的效果;绿原酸则具有强抗氧化能力,通过抑制三酰甘油的合成来调节脂质代谢。前人的研究结果表明蚊母树乙酸乙酯提取物对能造成感染性肥胖的人腺病毒36的显著增殖有抑制作用,对体外脂质积累具有抑制作用;创伤酸可以抑制脂肪细胞中脂质积聚,以减轻高脂肪饮食诱导的肥胖。本研究进一步明确了蚊母树和小叶蚊母树有发挥降脂作用的活性成分,有望进一步用于开发感染性肥胖治疗剂[11-12, 15-16]。此外,还挖掘到具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤、治疗神经系统疾病等高活性的黄酮类化合物[19]山奈酚、槲皮素和苯丙素类化合物绿原酸;具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗肿瘤、降低胆固醇、减肥等生物学功能的高生物活性的多酚类化合物表没食子儿茶素[21];具有修复心肌细胞缺氧、复氧损伤和抑制肝纤维化活性的表儿茶素[17-18];具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抑菌、降血脂、保护心血管等作用的丹叶大黄素[20]。用于治疗小儿急性淋巴细胞白血病的主要成分之一6-巯基嘌呤[22],人体必需氨基酸L-苯丙氨酸和色氨酸,L-精氨酸,具有抗氧化、增强免疫和促进肠道健康等活性。其中京尼平苷酸、山奈酚、槲皮素、6-巯基嘌呤和各氨基酸在蚊母树差异代谢产物中显著上调,琥珀酸、3-羟基甲基苯甲酸、绿原酸、创伤酸、丹叶大黄素和表没食子儿茶素在小叶蚊母树差异代谢产物中显著上调,这说明蚊母树和小叶蚊母树在各自药理活性上会存在一定侧重差异,并为小叶蚊母树和蚊母树的潜在药效挖掘提供多个较为准确的方向指引。对于是否具有上述药理活性及其活性强弱,仍需进行相应药理实验加以验证。
经过对差异代谢产物含量及代谢通路分析,发现小叶蚊母树中茉莉酸含量为蚊母树中茉莉酸含量的12.68倍,茉莉酸是一种对生物和非生物胁迫做出快速反应的激素,可作为信号分子诱导机体产生系列抗逆反应,保护机体,其下游产物包括创伤素、创伤酸、茉莉酸盐和茉莉酸甲酯等[25-31],可促进植物伤口愈合,阻止病原体进一步入侵,在植物防御过程中起着关键作用。有报道显示[34-39],外源性应用茉莉酸可减轻辣椒疫霉Phytophthora capsici 感染症状,提高水稻Oryza sativa对稻瘟病的抗性,激活红麻Apocynum venetum抗根结线虫Meloidogyne javanica相关基因NPR1的表达,从而激活植物系统抗性(induced systemic resistance,ISR);此外,外源茉莉酸甲酯处理可影响紫花苜蓿Medicago sativa的防御酶活性及单宁含量,进而提高紫花苜蓿抗蓟马性[40];另外,可抑制茶Camellia sinensis 树茶尺蠖Geometrid larvae幼虫的生长[25]。结合已有研究结果分析,认为小叶蚊母树中高水平的茉莉酸含量可能是小叶蚊母树几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的主要原因之一,外源应用植物激素可增强植物抗逆、抗病、抗虫性,茉莉酸外源应用可能成为蚊母树虫瘿防治的有效手段。
本研究基于广泛靶向代谢组学从蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的共性成分中挖掘出具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗菌、抗肿瘤、降压、降脂、抑制肝纤维化、心肌细胞缺氧保护、增强免疫、促进肠道健康、治疗糖尿病和小儿急性淋巴细胞白血病等药理活性的多个成分,为蚊母树和小叶蚊母树的药用开发提供方向和参考。但未能挖掘到具有明确吸引或驱避虫瘿寄生的次生代谢产物,结合代谢通路的显著差异程度分析和现有研究结果,认为较高水平的茉莉酸含量可能是小叶蚊母树几乎不受虫瘿寄生危害的主要原因之一。
-
表 1 小叶蚊母树和蚊母树差异代谢产物相对含量(≥0.5%)统计
Table 1 Statistical table of relative content of differential metabolites (≥0.5%) in D. racemosum and D. buxifolium
ID 代谢物名称 相对含量
(Db)/%相对含量
(Dr)/%含量比值
(Dr/Db)ratio VIP 类型 pos-M175T253 alpha-Ionene 0.11 1.21 11.13 6.84 1.82 up neg-M169T73 没食子酸 2.04 12.70 6.23 4.11 1.50 up pos-M111T258 2,4-辛二烯 0.00 0.46 186.60 114.80 2.79 up pos-M129T258 (R)-Sulcatol 0.01 0.53 91.90 56.54 2.57 up neg-M373T221 京尼平苷酸 0.32 1.78 5.55 3.42 1.30 up pos-M145T263 2-甲基庚酸 1.64 5.93 3.61 2.22 1.08 up pos-M180T64 3-羟基甲基苯甲酸 2.18 1.71 0.79 0.48 1.03 down neg-M293T425 (9Z,12Z,14E)-16-Hydroxy-9,12,14-octadecatrienoic acid 0.49 0.14 0.28 0.17 1.36 down neg-M293T401 9-HOTrE 2.36 0.64 0.27 0.17 1.23 down pos-M275T413 诺龙 0.49 0.08 0.16 0.15 1.36 down pos-M291T323 (9Z,11E,13E,15Z)-4-Oxo-9,11,13,15-octadecatetraenoic acid 0.79 0.08 0.10 0.08 1.43 down neg-M225T290 3,4-Methylenesebacic acid 1.97 0.15 0.07 0.05 2.01 down neg-M227T276 愈伤酸 2.83 0.12 0.04 0.03 2.10 down neg-M209T276 茉莉酸 2.51 0.20 0.08 0.03 2.17 down neg-M211T337 Traumatin 1.03 0.04 0.04 0.03 2.00 down neg-M323T332 Cibaric acid 0.95 0.03 0.03 0.02 2.22 down neg-M291T392 (2'E,4'Z,7'Z,8E)-Colnelenic acid 4.14 0.17 0.04 0.01 2.09 down neg-M307T349 Corchorifatty acid D 2.59 0.13 0.05 0.01 2.13 down pos-M130T79 2-哌啶甲酸 0.08 0.95 12.67 11.30 1.92 up pos-M175T43 L-精氨酸 0.20 2.95 14.78 9.09 1.88 up pos-M166T182 L-苯丙氨酸 0.89 5.71 6.41 3.94 1.51 up pos-M132T103 异亮氨酸 0.65 3.05 4.69 2.88 1.23 up neg-M133T43 D-(+)-苹果酸 3.64 2.57 0.70 0.44 1.12 down neg-M191T188 D-(-)-奎宁酸 2.80 1.62 0.58 0.36 1.24 down neg-M117T57 琥珀酸 2.09 0.85 0.41 0.25 1.53 down pos-M184T64 磷酸胆碱 0.26 0.99 3.78 5.50 1.64 up pos-M289T188 Phlorin 0.53 1.75 3.33 2.05 1.05 up neg-M402T195 2,4-Dihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-
one 2-glucoside0.03 2.28 66.35 40.82 2.49 up neg-M179T261 表肌醇 0.03 0.79 24.03 14.78 2.10 up neg-M415T218 2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde O-[xylosyl-(1->6)-glucoside] 0.13 0.90 6.91 4.25 1.47 up pos-M261T38 D-肌醇-4-磷酸 0.56 0.47 0.85 0.52 1.02 down neg-M353T200 绿原酸 5.38 1.14 0.21 0.13 1.85 down neg-M207T291 (Z)-3-Oxo-2-(2-pentenyl)-1-cyclopenteneacetic acid 0.68 0.06 0.09 0.04 2.06 down pos-M153T217 6-巯基嘌呤 0.23 3.27 14.34 3.97 1.35 up pos-M188T200 3-吲哚丙烯酸 0.48 2.88 6.05 3.72 1.49 up pos-M205T200 L-色氨酸 0.31 1.85 5.94 3.66 1.47 up pos-M86T103 六氢吡啶 0.21 0.90 4.34 2.67 1.16 up pos-M85T64 呋喃酮 A 0.79 0.59 0.75 0.46 1.05 down neg-M243T382 枇杷呋喃 4.00 2.41 0.60 0.37 1.53 down neg-M111T43 糠酸 0.60 0.35 0.58 0.36 1.18 down neg-M143T49 2-甲基-5-甲硫基噻吩 0.33 0.21 0.62 0.38 1.27 down pos-M287T257 山奈酚 0.85 6.76 7.99 4.91 1.63 up pos-M303T247 槲皮素 0.68 2.96 4.38 2.69 1.29 up neg-M305T210 表没食子儿茶素 1.37 0.83 0.60 0.37 1.15 down pos-M163T190 3-羟基香豆素 3.26 1.12 0.34 0.21 1.52 down neg-M257T351 丹叶大黄素 4.44 1.30 0.29 0.18 1.79 down neg-M289T219 表儿茶素 6.17 1.26 0.20 0.13 1.84 down pos-M287T332 橡精 0.11 0.84 7.47 7.88 1.88 up neg-M403T219 Oleoside 11-methyl ester 0.22 0.99 4.43 2.15 1.07 up neg-M309T379 9-Oxo-11-(3-pentyl-2-oxiranyl)-10E-undecenoic acid 11.54 0.52 0.05 0.03 2.09 down -
[1] 李晓腾,刘世彪,张世鑫,等. 中华蚊母树虫瘿类型及其致瘿昆虫生活史初探[J]. 昆虫知识,2010,47(4):789 − 793. [2] 付素静,刘胜梅,莫大美,等. 生长激素对蚊母树扦插繁殖效果的影响[J]. 南方农业学报,2013,44(7):1160 − 1164. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2013.7.1160 [3] 何张齐,杨先裕,练发良,等. ‘丽玫’小叶蚊母树夏季不同位置叶片表型差异及光合特性研究[J]. 浙江林业科技,2017,37(2):76 − 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3776.2017.02.012 [4] 刘泽彬,程瑞梅,肖文发,等. 中华蚊母树(Distyliumchinense)幼苗对秋、冬季淹水的生长及生理响应[J]. 湖泊科学,2016,28(2):405 − 413. [5] 崔哲,沈光海. 蚊母树化学成分的研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(66):126. [6] 张敏,何衍彪,李意成,等. 蚊母树和小叶蚊母树嫩叶挥发性成分差异分析[J]. 现代园艺,2023,46(13):38 − 40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2023.13.013 [7] 龙娟,徐湘潭,何衍彪,等. 蚊母新胸蚜化学防治药剂筛选试验[J]. 现代园艺,2023,46(13):112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4958.2023.13.038 [8] 吴玲,李珊珊,黄玉娟,等. 6种金缕梅科植物挥发性成分动态变化及抑菌效果研究[J]. 林业与环境科学,2023,39(3):67 − 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4427.2023.03.009 [9] DUAN X X,QIN D,SONG H C,et al. Irpexlacte A-D,four new bioactive metabolites of endophytic fungus irpexlacteus DR10-1 from the waterlogging tolerant plant distyliumchinense[J]. Phytochemistry Letters,2019,32:151 − 156.
[10] LEE J S, NAM Y J, YANG J,et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of distylium racemosum extract in a mouse model of allergic asthma[J]. Planta Medica International Open,2018,5(2):48 − 54. doi: 10.1055/a-0600-9786
[11] KIM H R,김혜란,YANG E J,et al. Antiviral effects of ethyl acetate fraction of distyliumracemosum leaf extract on adenovirus 36[J]. 생명과학회지,2020,30(3).
[12] KIM H R,JUNG B K,YEO M H,et al. Inhibition of lipid accumulation by the ethyl acetate fraction of distyliumracemosum in vitro and in vivo[J]. Toxicology Reports,2019,6(6):215 − 221.
[13] LIU M J,JIN F J, ZHANG S, et al. Activation of farnesoid X receptor signaling by geniposidic acid promotes osteogenesis[J]. Phytomedicine,2022,103:154258.
[14] LIU L B,ZHANG C Y,ZHAI M, et al. Effect of chlorogenic acid on lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 cells induced by oxidative stress[J]. Food Bioscience,2023,51.
[15] 沈创鹏,黄丽平,项华,等.三黄降糖片及其主要成分对羟甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶的抑制作用[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2016,18(4):23 − 25. [16] GAO J F,ZHANG Z X,DONG X H, et al. Traumatic acid inhibits ACSL4 associated lipid accumulation in adipocytes to attenuate high-fat diet-induced obesity[J]. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology,2023,37(12):e23278 − e23278.
[17] 俞超楠. 表儿茶素抑制HMGB1信号通路修复心肌细胞缺氧/复氧损伤[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2020,37(12):2418 − 2423. [18] 王玉涵,展凡,程卉,等. 表儿茶素对四氯化碳诱导肝纤维化大鼠的干预作用[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2020,39(1):50 − 55. [19] 李明奇,赵晓璐,高晓阳,等.植物药总黄酮的药理作用机制及应用进展[J/OL]. 中华中医药学刊,1 − 15 [2023-11-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20230705.1603.002.html. [20] 柯辛格. 丹叶大黄素对非酒精性脂肪肝的药理作用及机制研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学,2021. [21] 李林竹,盛赵越,李艺,等. 表没食子儿茶素-壳聚糖纳米乳液的制备及其性能分析[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(5):254 − 259. [22] 魏娜,郑斌,庄茜,等. 巯嘌呤甲基转移酶基因检测用于指导6-巯基嘌呤在中国儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病中个体化治疗的循证评价[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2020,37(17):2159 − 2167. [23] 匡美美,李黎,马建伟,等.利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J/OL]. 园艺学报,1 − 14 [2024-06-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1924.S.20240530.1035.002.html. [24] 徐伟,严善春. 茉莉酸在植物诱导防御中的作用[J]. 生态学报,2005(8):2074 − 2082. [25] 桂连友,陈宗懋,刘树生. 外源茉莉酸甲酯处理茶树对茶尺蠖幼虫生长的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2005,(2):302 − 307. [26] 孙凯迪,蒯鹏,吕静,等. 外施多效唑诱导水稻对稻飞虱的抗性[J]. 昆虫学报,2024,67(4):549 − 558. [27] 冯振,郑春燕,薄玉琨,等. 基于转录组和代谢组探究植物应答干旱和植食性昆虫的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2024,32(03):369 − 379. [28] 孙雨桐,刘德帅,齐迅,等. 茉莉酸调控植物生长发育和胁迫的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报,2023,39(11):99 − 109. [29] 张旸,孙天旭,郭勃予,等. 羊草脂氧合酶同源蛋白基因LcLHP的克隆与表达分析[J]. 华北农学报,2015,30(4):35 − 42. [30] 张福彦,陈锋,张建伟,等. 逆境胁迫下小麦脂肪氧化酶基因表达的qRT-PCR分析[J]. 麦类作物学报,2016,36(9):1153 − 1158. [31] 笪远峰,戚雪勇. β-取代丙烯酸的合成研究[J]. 化学世界,1998,(4):6 − 9. [32] NETO C G, KONO Y, HYAKUTAKE H, et al. Isolation and Identification of (–)-Jasmonic acid from wild rice, oryza officinalis, as an antifungal substance[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry,2014,55(12): 3097-3098.
[33] 巨云为,朱萍,施大伟,等. 蚊母树对杭州新胸蚜虫瘿形成的生理生化响应[J]. 福建林学院学报,2012,32(1):10 − 12. [34] 刘爽,李珅,王东梅,等. 基于大刍草渗入系的玉米抗旱优异等位基因挖掘[J/OL]. 作物学报,1 − 11 [2024-06-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1809.s.20240418.1149.002.html. [35] 胡亚群,周琰琰,武婷,等. VrJAZ1和VrJAZ12在绿豆对群结腐霉抗性中的功能研究[J/OL]. 南京农业大学学报,1 − 12 [2024-06-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1148.S.20240520.1710.004.html. [36] 苟亚峰,田甜,温思为,等. 硬枝黄蝉中四种环烯醚萜类化合物对辣椒疫霉菌的抑菌活性研究[J/OL]. 热带农业科学,1 −4 [2024-06-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1038.s.20240603.1050.002.html. [37] KATTUPALLI D,PINSKI A,SREEKUMAR S,et al. Non-Targeted metabolite profiling reveals host metabolomic reprogramming during the interaction of black pepper with phytophthora capsic[J]. International Journal of Molecular Science,2021,22(21):11433. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111433
[38] 陈玲,杨长登,梁燕,等. 粮食作物真菌类病害及其抗性鉴定方法研究进展[J/OL]. 浙江农业科学,1 − 12 [2024-06-04]. https://doi.org/10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20230852. [39] 刘勇,杨志晓,孔德钧,等. 烟草NPR1基因家族鉴定及其在南方根结线虫胁迫下的表达分析[J/OL]. 山东农业科学,1 − 15 [2024-06-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/37.1148.S.20240528.1742.002.html. [40] 爽爽,霍晓伟,陈崎,等. 茉莉酸甲酯对苜蓿抗蓟马性及其生理指标的影响[J]. 中国草地学报,2024,46(5):82 − 90.



 下载:
下载: