High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image Forest Land Change Detection Based on Deep Learning
-
摘要:
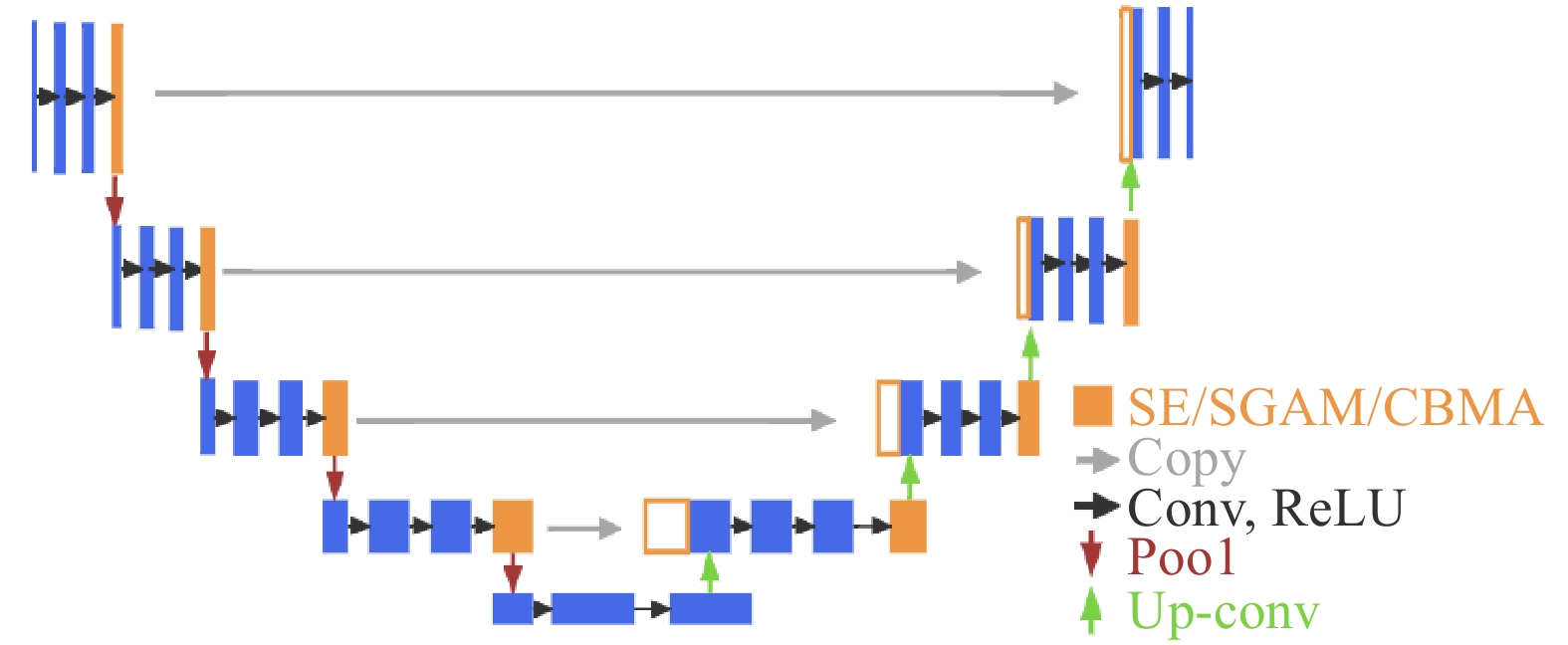
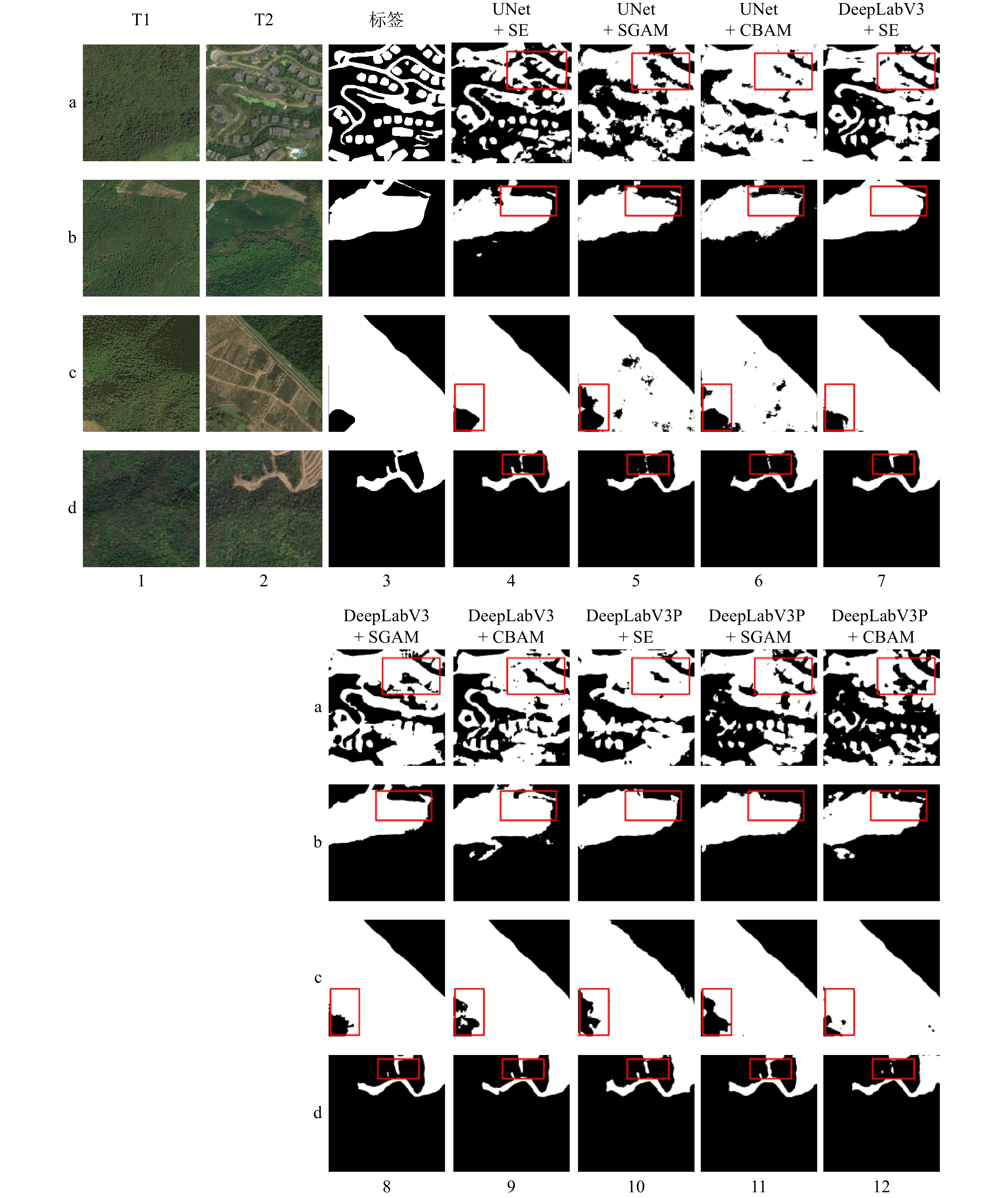
基于深度学习进行的高分辨率遥感影像林地变化检测,能通过大规模数据训练从双时相高分影像中自动提取林地变化特征,可减少对操作人员的主观经验性依赖,提高林地变化检测效率。本文以浙江省为研究区域,基于World Imagery Wayback高分辨率遥感图像,利用UNet系列、DeepLabV3系列、FCN及SegNet等深度学习模型,通过二分类方法判断林地变化范围。结果表明:(1)本文所使用的各种模型,在测试集上mIoU评估指标均在84.70%以上,Accuracy指标均在92.00%以上,F1-score评估指标均在91.00%以上,Recall评估指标也均在91.00%以上,表现出较好的检测结果。(2)UNet模型各项指标均达到最高,mIoU、Accuracy、F1-score和Recall评估指标分别为89.54%、95.15%、94.44%及94.13%,但各模型在检测结果中均存在不同程度的边缘轮廓模糊、类内连通不完整现象。(3)为解决检测结果中存在的类内连通不完整及轮廓模糊问题,利用SE、SGAM、CBAM等注意力机制改进性能很好的UNet模型,为验证模型改进的有效性以及排除模型结构差异的影响,对DeepLabV3、DeepLabV3P模型也做相同的改进,以形成对照实验。结果显示,利用通道注意力机制改进的UNet+SE模型mIoU指标提高最多,为0.18%。但利用空间注意力机制改进的UNet+SGAM、DeepLabV3+SGAM、DeepLabV3P+SGAM模型,其mIoU指标分别降低了1.01%、0.77%、0.67%,因此在检测林地变化时,通道上的特征重要性大于空间上的特征重要性,需加重关注通道特征,降低关注空间特征。基于深度学习进行的高分辨率遥感影像林地变化检测,在各模型中UNet模型的性能指标表现优秀,且模型的通道重要性大于空间重要性,该结论可为林地变化检测提供重要借鉴。
Abstract:Deep learning offers an efficient approach to forest land change detection by automatically extracting change features from dual-time-phase high-resolution images through large-scale data training, reducing reliance on operator experience and enhancing detection efficiency. Focusing on Zhejiang Province, this study utilized high-resolution remote sensing images from World Imagery Wayback and applied deep learning models, including UNet series, DeepLabV3 series, FCN, and SegNet, for binary classification of forest land changes. All models demonstrated strong performance on the test set, with mIoU above 84.70%, Accuracy above 92%, F1-score above 91.00%, and Recall above 91%. Among them, the UNet model achieved the best results, with mIoU of 89.54%, Accuracy of 95.15%, F1-score of 94.44%, and Recall of 94.13%, though all models showed varying degrees of edge contour blurring and incomplete intra-class connectivity. To address these limitations, the UNet model was improved using attention mechanisms, including SE (Squeeze-and-Excitation), SGAM (Spatial Gated Attention Mechanism), and CBAM (Convolutional Block Attention Module), and similar enhancements were applied to DeepLabV3 and DeepLabV3P models for control experiments. Results showed that the UNet+SE model, leveraging channel attention, achieved the greatest improvement in mIoU (0.18%), while models enhanced with spatial attention (UNet+SGAM, DeepLabV3+SGAM, DeepLabV3P+SGAM) experienced decreases in mIoU by 1.01%, 0.77%, and 0.67%, respectively, indicating that channel features are more critical than spatial features for forest land change detection. These findings confirm the UNet model’s superior performance and highlight the importance of prioritizing channel features, providing valuable insights for forest land change detection using deep learning and high-resolution remote sensing imagery.
-
Keywords:
- Woodland /
- deep learning /
- high-resolution remote sensing /
- change detection
-
-
表 1 双时相遥感影像基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of dual temporal remote sensing images
影像范围 影像名称 数据源版本 分辨率/m 波段 地理坐标系 湖州市 前期遥感影像 Wayback 2018-12-14 0.5 R、G、B WGS 84 湖州市 后期遥感影像 Wayback 2023-12-07 0.5 R、G、B WGS 84 表 2 各模型在测试数据集评估指标
Table 2 Evaluation metrics of each model on the test data set
模型名称 mIoU/% Accuracy/% Kappa/% F1-score/% Precision/% Recall/% UNet[17] 89.54 95.15 88.89 94.44 94.79 94.13 AttentionUNet[18] 88.93 94.85 88.20 94.10 94.52 93.72 BiseNetV1[19] 88.93 94.85 88.20 94.10 94.52 93.71 UNet++[20] 88.92 94.82 88.19 94.09 94.29 93.91 CCNet[21] 88.72 94.75 87.97 93.98 94.44 93.57 DeepLabV3[22] 88.51 94.63 87.72 93.86 94.16 93.59 DANet[23] 88.25 94.52 87.43 93.71 94.16 93.31 DeepLabV3P[24] 88.24 94.53 87.41 93.70 94.31 93.17 U2Net[25] 88.04 94.39 87.18 93.59 93.90 93.30 SegNet[26] 87.96 94.38 87.09 93.54 94.10 93.05 PSPNet[27] 87.46 94.10 86.51 93.25 93.56 92.98 UNet3+[28] 86.75 93.76 85.68 92.84 93.29 92.44 BiSeNetV2[29] 86.25 93.57 85.10 92.55 93.54 91.73 FCN[30] 84.88 92.73 83.49 91.75 91.75 91.75 FastSCNN[31] 84.72 92.71 83.29 91.65 92.14 91.28 注:加粗值代表该列最高指标。 表 3 模型改进后的各项评估指标
Table 3 Evaluation metrics of the improved model
模型名称 mIoU/% Accuracy/% Kappa/% F1-score/% Precision/% Recall/% UNet (原始) 89.54 95.15 88.89 94.44 94.79 94.13 UNet + SE 89.72 95.24 89.09 94.54 95.01 94.12 UNet + SGAM 88.53 94.65 87.75 93.87 94.25 93.53 UNet + CBAM 87.21 93.96 86.23 93.12 93.23 93.01 DeepLabV3 (原始) 88.51 94.63 87.82 93.86 94.16 93.59 DeepLabV3 + SE 88.56 94.66 87.78 93.89 94.22 93.58 DeepLabV3 + SGAM 87.74 94.26 86.83 93.41 93.87 93.00 DeepLabV3 + CBAM 87.94 94.37 87.07 93.53 94.06 93.07 DeepLabV3P (原始) 88.24 94.53 87.41 93.70 94.31 93.17 DeepLabV3P + SE 86.45 93.62 85.34 92.67 93.20 92.19 DeepLabV3P + SGAM 87.57 94.18 86.64 93.32 93.86 92.83 DeepLabV3P + CBAM 86.94 93.80 85.91 92.96 92.98 92.94 注:加粗值代表该列最高指标。 表 4 模型改进后各项评估指标的增减情况
Table 4 Changes in evaluation metrics after model improvement
模型名称 mIoU/% Accuracy/% Kappa/% F1-score/% Precision/% Recall/% UNet + SE +0.18 +0.09 +0.20 +0.10 +0.22 −0.01 UNet + SGAM −1.01 −0.50 −1.14 −0.57 −0.54 −0.60 UNet + CBAM −2.33 −1.19 −2.66 −1.32 −1.56 −1.12 DeepLabV3 + SE +0.05 +0.03 +0.06 +0.03 +0.06 −0.01 DeepLabV3 + SGAM −0.77 −0.37 −0.89 −0.45 −0.29 −0.59 DeepLabV3 + CBAM −0.57 −0.26 −0.65 −0.33 −0.10 −0.52 DeepLabV3P + SE −1.79 −0.91 −2.07 −1.03 −1.11 −0.98 DeepLabV3P + SGAM −0.67 −0.035 −0.77 −0.38 −0.45 −0.34 DeepLabV3P + CBAM −1.30 −0.73 −1.50 −0.74 −1.33 −0.23 注:+加粗代表指标提高,−代表指标降低。 -
[1] 郭琦. 林业资源保护与森林防火管理的重要性及对策[J]. 农业与技术,2021,41(12):71 − 73. [2] 王帆. 基于高分遥感的林地动态变化检测算法研究[D]. 西安:西安科技大学,2021. [3] 周启鸣. 多时相遥感影像变化检测综述[J]. 地理信息世界,2011,9(02):28 − 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2011.02.007 [4] 林帅,刘会欣,张强,等. 张家口市植被指数变异及动态变化特征分析[J]. 农业技术与装备,2022(3):49 − 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-887X.2022.03.018 [5] 乐颖,夏元平. 基于比值法的多源多时相数据城区变化检测[J]. 测绘通报,2022(2):56 − 61. [6] 李福根,张保辉,段玉林. 利用植被指数非相似性监测水稻病虫害方法研究[J]. 中国农业信息,2020,32(1):46 − 63. [7] SOLTANINEJAD M,JAFARI M,NOROOZI A,et al. Evaluation of vegetation changes in desertification projects using remote sensing techniques in bam,shahdad and garmsar regions,Iran[J]. Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences,2021,19(1):47 − 57.
[8] ZHANG Y,JIANG F. Developing a remote sensing-based ecological index based on improved biophysical features[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing,2021,16(1):012008 − 012008.
[9] SHNAIN S. Features extraction of lands at 7 images using tasseled cap transformation[J]. Journal of Al-Rafidain University College For Sciences,2021(1):215 − 223.
[10] SRISUK S,ARUNYAGOOL D,PETCHTHAWEETHAM B. Fast change detection based on GPGS-PCA[C]//2020 8th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON). IEEE,2020:1 − 4.
[11] 王鹏. 遥感影像的ISODATA分类算法的并行化研究[D]. 开封:河南大学,2016. [12] 齐永菊,裴亮,张宗科,等. 一种模糊聚类的遥感影像分析方法研究[J]. 测绘科学,2017,42(7):139 − 146. [13] PAN H Y ,TONG X H,XU X,et al. Updating of land cover maps and change analysis using globe land 30 Product:a case study in shanghai metropolitan area,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(19):3147 − 3147. doi: 10.3390/rs12193147
[14] WANG J,ZHANG J X,ZHANG R. An integrated method for change detection and map updating based on decision tree rules[J]. Remote Sensing Information,2007,1(4):61 − 65.
[15] LIU X,GUO Y A. Remote sensing image change detection algorithm based on random forest[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2022(5):16 − 20.
[16] LECUN Y ,BOTTOU L . Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE,1998,86(11):2278 − 2324.
[17] RONNEBERGER O,FISCHER P,BROX T. U-net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer,Cham,2015:234 − 241.
[18] OKTAY O,SCHLEMPER J,FOLGOc L L,et al. Attention U-Net:Learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. [2024-03-20],http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999?sid_for_share=99125_3.
[19] YU C Q, WANG J B,PENG C,et al. BiSeNet:Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation[J]. Computer Vision-ECCV 2018:15th European Conference,2018(11217):334 − 349.
[20] ZHOU ZW,MD M R S,NIMA T,et al. Unet plus plus:a nested U-net architecture for medical image segmentation[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science,2018(11045):3 − 11.
[21] HUANG Z L, WANG X G, WEI Y C,et al. CCNet:Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE,2023,45(6):6896 − 6908. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3007032
[22] CHEN L C,PAPANDREOU G,SCHROFF F,et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. [2024-02-13],https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587?sid_for_share=99125_3.
[23] FU J,LIU J ,TIAN H J,et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[J]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),2019(02983):3141 − 3149.
[24] LIANG CC,YUKUN Z,GEORGE P,et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision,2018,11211:833 − 851.
[25] QIN X,ZHANG Z,HUANG C,et al. U 2 -Net:Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition,2020,106(C):107404 − 107404.
[26] VIJAY B,ALEX K,ROBERTO C. SegNet:A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,2017,39(12):2481 − 2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
[27] ZHAO H S,SHI J P,QI X J,et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[J]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),2017(01105):6230 − 6239.
[28] HUANG H M,LIN L F,TONG R F,et al. Unet 3+:a full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing,2020,abs/2004.08790:1055 − 1059.
[29] YU C,GAO C,WANG J,et al. BiseNet V2:bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation[J]. Springer US,2021(129):3051−3068.
[30] WANG J,SUN K,CHENG T,et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2021,43(10):3349 − 3364. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2983686
[31] POUDEL K P R,LIWICKI S,CIPOLLA R. Fast-SCNN:Fast semantic segmentation network[J]. British Machine Vision Conference,2019(04502):289 − 289.
[32] HU J,SHEN L,SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018:7132 − 7141.
[33] WOO S,PARK J,LEE J Y,et al. Cbam:Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018:3 − 19.
[34] 艾遒一,黄华国,郭颖,等. 基于孪生残差神经网络的GF-2影像林地变化检测——以浙江省建德林场为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用,2024,39(1):24 − 33.




 下载:
下载: